1.
The Intangible in Human Progress
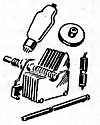 Suppose, in our imagination, we take this radio apart. Suppose we take
all the pieces out of the wooden box we call a cabinet. Now, you could call in a good cabinetmaker
and say, "Jim, can you make a cabinet like that for me?" He'd answer
you, "Of course I can. For about five dollars." You could say to
another fellow, "How much can you make that pin for?" He might say,
"Oh, about a dime."
Suppose, in our imagination, we take this radio apart. Suppose we take
all the pieces out of the wooden box we call a cabinet. Now, you could call in a good cabinetmaker
and say, "Jim, can you make a cabinet like that for me?" He'd answer
you, "Of course I can. For about five dollars." You could say to
another fellow, "How much can you make that pin for?" He might say,
"Oh, about a dime."
Then you look at all the parts on the table.
Someone had to make every piece in the set. If you checked only the
weight of the material, you'd probably find the radio could be bought
for forty or fifty cents a pound. But you can't buy a radio the way you
buy a pound of meat. That material isn't all you bought. You bought
something else. You bought that intangible something which, when the
parts are all put together, makes it work. That something which makes
it possible for you to hear the announcer say, "This is London calling."
 When you bought that radio you bought the combined knowledge and
experience of every great electrical scientist from Michael Faraday on
down to the present. You also bought the results of endless experiments
and the ideas of thousands of inventors.
When you bought that radio you bought the combined knowledge and
experience of every great electrical scientist from Michael Faraday on
down to the present. You also bought the results of endless experiments
and the ideas of thousands of inventors.
That is what is housed in that cabinet along
with so many pounds of material - that intangible some-thing which goes
into every product - that something which is priceless.
|