Part of a series of articles for National Chemistry Week 2023 on
Unveiling the Surprising Healing Power of Chemistry
Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy is a medical treatment that exemplifies the profound influence of chemistry in healthcare, providing an unexpected method for managing specific medical conditions, notably heavy metal poisoning and cardiovascular health issues. At its core, chelation therapy is based on the chemistry of chelating agents, which are compounds capable of binding and removing toxic heavy metals from the body.
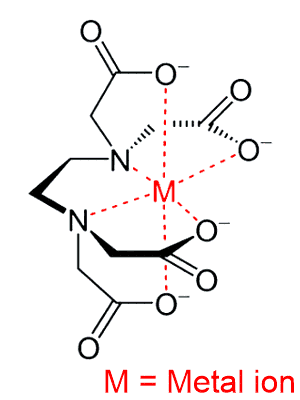
The chemistry behind chelation therapy begins with the selection of a chelating agent. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is the most commonly employed chelating agent in this context. EDTA has a remarkable ability to form stable complexes with heavy metal ions due to its hexadentate structure. It possesses six binding sites that can encircle and trap toxic metals, such as lead, mercury, and cadmium.
The process of chelation therapy involves the administration of a chelating agent, often through intravenous infusion. Once introduced into the bloodstream, the chelating agent circulates throughout the body, where it encounters and binds to heavy metal ions. The resulting complexes are then excreted from the body via urine, effectively removing the toxic metals.
Chelation therapy has found critical application in cases of heavy metal poisoning, particularly lead poisoning, which can result from exposure to lead-based paints, contaminated water, or occupational hazards. The chemistry of chelation effectively reduces the body’s burden of toxic metals and mitigates the potential health consequences, which can include neurological damage and organ dysfunction.
Beyond heavy metal poisoning, chelation therapy has garnered attention for its potential role in cardiovascular health. Some proponents of chelation therapy argue that it can remove calcium deposits from arterial walls, thereby improving blood flow and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. The chemistry behind this hypothesis lies in the ability of chelating agents to bind with calcium ions and facilitate their removal from tissues.
However, it is essential to note that the use of chelation therapy for cardiovascular health remains a subject of debate within the medical community, with clinical evidence providing mixed results. While the chemistry behind the binding of calcium by chelating agents is well-established, the overall efficacy and safety of this approach for heart health require further investigation.
Chelation therapy underscores the critical role of chemistry in medicine, offering an unexpected method for treating heavy metal poisoning and exploring potential applications in cardiovascular health. As research continues to unravel the intricate chemistry of chelating agents and their interactions within the body, we can anticipate a better understanding of the therapy’s scope, safety, and effectiveness in addressing a range of health concerns.