The
differential hydrostatic wheel
A, B, C, D are
four vessels connected to the wheels, E, by round pins which project
from the vessels on each side, and enter into corresponding holes in
the wheels E. The wheels, E, are intended to revolve by the space under
the vessel, B, being a vacuum, and therefore lighter than the same
portion of air; a little before the vessel, B, reaches the highest
point of the wheels, it begins to close, and opens the opposite vessel,
D, in the same manner as the vessel, C, opens A, because the pressure
of the atmosphere on the vessel, C, is equal to the pressure on A.
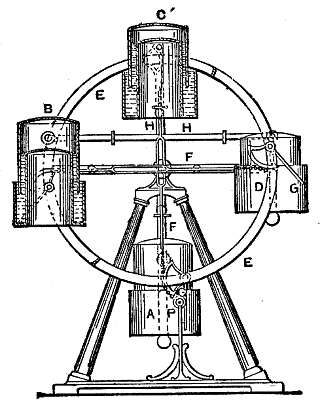
Instead
of common packing to make the vessels air-tight, mercury is
substituted, which has less friction, and is never out of order. The
particles of mercury not being entirely free from friction, a little
power is requisite to open and shut the vessels; this is expected to be
effected by the rods, F, connected to the lever, G, by chains. The
rods, F, give motion to other rods, H, by the rollers acting against
collars on the rods, H, not shown.
The levers, G, are successively worked by sliding over the roller P. The connecting rods, H, are so adjusted as not to draw the vessels out of their upright position, which would let the mercury escape; also, the lower vessels, A and D, are made rather larger in diameter than B, C, so that the pressure of the atmosphere may counterpoise the weight of the vessels, A, C and B, D; with their connecting rods.
The levers, G, are successively worked by sliding over the roller P. The connecting rods, H, are so adjusted as not to draw the vessels out of their upright position, which would let the mercury escape; also, the lower vessels, A and D, are made rather larger in diameter than B, C, so that the pressure of the atmosphere may counterpoise the weight of the vessels, A, C and B, D; with their connecting rods.
(Subsection 929, from
p.371)
From: Gardner D. Hiscox, M.E., Mechanical Appliances and Novelties of Construction (1927), Norman W. Henley Publ. Co.