According Quotes (236 quotes)
...That day in the account of creation, or those days that are numbers according to its recurrence, are beyond the experience and knowledge of us mortal earthbound men. And if we are able to make any effort towards an understanding of those days, we ought not to rush forward with an ill considered opinion, as if no other reasonable and plausible interpretation could be offered.
iv.44
“Conservation” (the conservation law) means this … that there is a number, which you can calculate, at one moment—and as nature undergoes its multitude of changes, this number doesn't change. That is, if you calculate again, this quantity, it'll be the same as it was before. An example is the conservation of energy: there's a quantity that you can calculate according to a certain rule, and it comes out the same answer after, no matter what happens, happens.
'The Great Conservation Principles', The Messenger Series of Lectures, No. 3, Cornell University, 1964. From transcript of BBC programme (11 Dec 1964).
“Science studies everything,” say the scientists. But, really, everything is too much. Everything is an infinite quantity of objects; it is impossible at one and the same time to study all. As a lantern cannot light up everything, but only lights up the place on which it is turned or the direction in which the man carrying it is walking, so also science cannot study everything, but inevitably only studies that to which its attention is directed. And as a lantern lights up most strongly the place nearest to it, and less and less strongly objects that are more and more remote from it, and does not at all light up those things its light does not reach, so also human science, of whatever kind, has always studied and still studies most carefully what seems most important to the investigators, less carefully what seems to them less important, and quite neglects the whole remaining infinite quantity of objects. ... But men of science to-day ... have formed for themselves a theory of “science for science's sake,” according to which science is to study not what mankind needs, but everything.
In 'Modern Science', Essays and Letters (1903), 223.
“These changes in the body,” he wrote in the review paper he sent to the American Journal of Physiology late in 1913, “are, each one of them, directly serviceable in making the organism more efficient in the struggle which fear or rage or pain may involve; for fear and rage are organic preparations for action, and pain is the most powerful known stimulus to supreme exertion. The organism which with the aid of increased adrenal secretion can best muster its energies, can best call forth sugar to supply the labouring muscles, can best lessen fatigue, and can best send blood to the parts essential in the run or the fight for life, is most likely to survive. Such, according to the view here propounded, is the function of the adrenal medulla at times of great emergency.”
Quoted in S. Benison, A. C. Barger and E. L. Wolfe, Walter B Cannon: The Life and Times of a Young Scientist (1987), 311.
[It has been ascertained by statistical observation that in engineering enterprises one man is killed for every million francs that is spent on the works.] Supposing you have to build a bridge at an expense of one hundred million francs, you must be prepared for the death of one hundred men. In building the Eiffel Tower, which was a construction costing six million and a half, we only lost four men, thus remaining below the average. In the construction of the Forth Bridge, 55 men were lost in over 45,000,000 francs’ worth of work. That would appear to be a large number according to the general rule, but when the special risks are remembered, this number shows as a very small one.
As quoted in 'M. Eiffel and the Forth Bridge', The Tablet (15 Mar 1890), 75, 400. Similarly quoted in Robert Harborough Sherard, Twenty Years in Paris: Being Some Recollections of a Literary Life (1905), 169, which adds to the end “, and reflects very great credit on the engineers for the precautions which they took on behalf of their men.” Sherard gave the context that Eiffel was at the inauguration [4 Mar 1890] of the Forth Bridge, and gave this compliment when conversing there with the Prince of Wales.
[Mathematics] has for its object the indirect measurement of magnitudes, and it proposes to determine magnitudes by each other, according to the precise relations which exist between them.
In The Positive Philosophy of Auguste Comte, translated by Harriet Martineau, (1896), Vol. 1, 40.
[On the 11th day of November 1572], in the evening, after sunset, when, according to my habit, I was contemplating the stars in a clear sky, I noticed that a new and unusual star, surpassing all others in brilliancy, was shining almost directly over my head; and since I had, almost from boyhood, known all the stars of the heavens perfectly (there is no great difficulty in gaining that knowledge), it was quite evident to me that there had never before been any star in that place in the sky, even the smallest, to say nothing of a star so conspicuously bright as this. I was so astonished at this sight that I was not ashamed to doubt the trustworthiness of my own eyes. But when I observed that others, too, on having the place pointed out to them, could see that there was a star there, I had no further doubts. A miracle indeed, either the greatest of all that have occurred in the whole range of nature since the beginning of the world, or one certainly that is to be classed with those attested by the Holy Oracles.
De Stello. Nova (On the New Star) (1573). Quoted in H. Shapley and A. E. Howarth (eds.), Source Book in Astronomy (1929), 13.
[Regarding evolution believers:] Their business is not with the possible, but the actual—not with a world which might be, but with a world that is. This they explore with a courage not unmixed with reverence, and according to methods which, like the quality of a tree, are tested by their fruits. They have but one desire—to know the truth. They have but one fear—to believe a lie.
'Scientific Use of the Imagination', Discourse Delivered Before the British Association at Liverpool, (16 Sep 1870). Fragments of Science for Unscientific People: A Series of Detached Essays, Lectures, and Reviews (1892), Vol. 2, 134.
[The] complex pattern of the misallocation of credit for scientific work must quite evidently be described as “the Matthew effect,” for, as will be remembered, the Gospel According to St. Matthew puts it this way: For unto every one that hath shall be given, and he shall have abundance: but from him that hath not shall be taken away even that which he hath. Put in less stately language, the Matthew effect consists of the accruing of greater increments of recognition for particular scientific contributions to scientists of considerable repute and the withholding of such recognition from scientists who have not yet made their mark.
'The Matthew Effect in Science', Science (1968), 159, 58.
[The] weakness of biological balance studies has aptly been illustrated by comparison with the working of a slot machine. A penny brings forth one package of chewing gum; two pennies bring forth two. Interpreted according to the reasoning of balance physiology, the first observation is an indication of the conversion of copper into gum; the second constitutes proof.
[Co-author with David Rittenberg (1906-70).]
[Co-author with David Rittenberg (1906-70).]
'The Application of Isotopes to the Study of Intermediary Metabolism', Science (1938), 87, 222.
[To] explain the phenomena of the mineral kingdom ... systems are usually reduced to two classes, according as they refer to the origin of terrestrial bodies to FIRE or to WATER; and ... their followers have of late been distinguished by the fanciful names of Vulcanists and Neptunists. To the former of these Dr HUTTON belongs much more than to the latter; though, as he employs the agency both of fire and water in his system, he cannot, in strict propriety, be arranged with either.
Illustrations of the Huttonian Theory of the Earth (1802) collected in The Works of John Playfair (1822), Vol. 1, 21
[W]e are prone to forget that the planet may be measured by man, but not according to man.
The Face of the Earth (1904), Vol. 1, 17.
Dilbert: It took weeks but I’ve calculated a new theory about the origin of the universe. According to my calculations it didn’t start with a “Big Bang” at all—it was more of “Phhbwt” sound. You may be wondering about the practical applications of the “Little Phhbwt” theory.
Dogbert: I was wondering when you’ll go away.
Dogbert: I was wondering when you’ll go away.
Dilbert comic strip (1 Jan 1993)
Dilbert: Wow! According to my computer simulation, it should be possible to create new life forms from common household chemicals
Dogbert: This raises some thorny issues.
Dilbert: You mean legal, ethical and religious issues?
Dogbert: I was thinking about parking spaces.
Dogbert: This raises some thorny issues.
Dilbert: You mean legal, ethical and religious issues?
Dogbert: I was thinking about parking spaces.
Dilbert comic strip (31 May 1989).
Les Leucocytes Et L'esprit De Sacrifice. — Il semble, d'après les recherches de De Bruyne (Phagocytose, 1895) et de ceux qui le citent, que les leucocytes des Lamellibranches — probablement lorsqu'ils ont phagocyté, qu'ils se sont chargés de résidus et de déchets, qu'ils ont, en un mot, accompli leur rôle et bien fait leur devoir — sortent du corps de l'animal et vont mourir dans le milieu ambiant. Ils se sacrifient. Après avoir si bien servi l'organisme par leur activité, ils le servent encore par leur mort en faisant place aux cellules nouvelles, plus jeunes.
N'est-ce pas la parfaite image du désintéressement le plus noble, et n'y a-t-il point là un exemple et un modèle? Il faut s'en inspirer: comme eux, nous sommes les unités d'un grand corps social; comme eux, nous pouvons le servir et envisager la mort avec sérénité, en subordonnant notre conscience individuelle à la conscience collective. (30 Jan 1896)
Leukocytes and The Spirit Of Sacrifice. - It seems, according to research by De Bruyne (Phagocytosis, 1885) and those who quote it, that leukocytes of Lamellibranches [bivalves] - likely when they have phagocytized [ingested bacteria], as they become residues and waste, they have, in short, performed their role well and done their duty - leave the body of the animal and will die in the environment. They sacrifice themselves. Having so well served the body by their activities, they still serve in their death by making room for new younger cells.
Isn't this the perfect image of the noblest selflessness, and thereby presents an example and a model? It should be inspiring: like them, we are the units of a great social body, like them, we can serve and contemplate death with equanimity, subordinating our individual consciousness to collective consciousness.
N'est-ce pas la parfaite image du désintéressement le plus noble, et n'y a-t-il point là un exemple et un modèle? Il faut s'en inspirer: comme eux, nous sommes les unités d'un grand corps social; comme eux, nous pouvons le servir et envisager la mort avec sérénité, en subordonnant notre conscience individuelle à la conscience collective. (30 Jan 1896)
Leukocytes and The Spirit Of Sacrifice. - It seems, according to research by De Bruyne (Phagocytosis, 1885) and those who quote it, that leukocytes of Lamellibranches [bivalves] - likely when they have phagocytized [ingested bacteria], as they become residues and waste, they have, in short, performed their role well and done their duty - leave the body of the animal and will die in the environment. They sacrifice themselves. Having so well served the body by their activities, they still serve in their death by making room for new younger cells.
Isn't this the perfect image of the noblest selflessness, and thereby presents an example and a model? It should be inspiring: like them, we are the units of a great social body, like them, we can serve and contemplate death with equanimity, subordinating our individual consciousness to collective consciousness.
In Recueil d'Œuvres de Léo Errera: Botanique Générale (1908), 194. Google translation by Webmaster. Please give feedback if you can improve it.
A bird is an instrument working according to mathematical law, which instrument it is within the capacity of man to reproduce with all its movements, but not with a corresponding degree of strength, though it is deficient only in the power of maintaining equilibrium. We may therefore say that such an instrument constructed by man is lacking in nothing except the life of the bird, and this life must needs be supplied from that of man.
'Of the Bird's Movement' from Codice Atlantico 161 r.a., in Leonardo da Vinci's Notebooks, trans. E. MacCurdy (1906), Vol. 1, 153.
A game is on, at the other end of this infinite distance, and heads or tails will turn up. What will you wager? According to reason you cannot leave either; according to reason you cannot leave either undone... Yes, but wager you must; there is no option, you have embarked on it. So which will you have. Come. Since you must choose, let us see what concerns you least. You have two things to lose: truth and good, and two things to stake: your reason and your will, your knowledge and your happiness. And your nature has two things to shun: error and misery. Your reason does not suffer by your choosing one more than the other, for you must choose. That is one point cleared. But your happiness? Let us weigh gain and loss in calling heads that God is. Reckon these two chances: if you win, you win all; if you lose, you lose naught. Then do not hesitate, wager that He is.
Pensées (1670), Section I, aphorism 223. In H. F. Stewart (ed.), Pascal's Pensées (1950), 117-119.
A man was famous according as he had lifted up axes upon the thick trees.
— Bible
Psalms 74:5 in Church of Scotland, The Book of Common-Prayer, and Administration of the Sacraments; and Other Parts of Divine Service For the Use of the Church of Scotland. With A Praphrase of the Psalms in Metre by King James the VI (1637), 250.
A man’s value to the community depends primarily on how far his feelings, thoughts, and actions are directed towards promoting the good of his fellows. We call him good or bad according to how he stands in this matter. It looks at first sight as if our estimate of a man depended entirely on his social qualities.
…...
A nutritive centre, anatomically considered, is merely a cell, the nucleus of which is the permanent source of successive broods of young cells, which from time to time fill the cavity of their parent, and carrying with them the cell wall of the parent, pass off in certain directions, and under various forms, according to the texture or organ of which their parent forms a part.
Anatomical and Pathological Observations (1845), 2.
A person who is religiously enlightened appears to me to be one who has, to the best of his ability, liberated himself from the fetters of his selfish desires and is preoccupied with thoughts, feelings, and aspirations to which he clings because of their superpersonal value. It seems to me that what is important is the force of this superpersonal content and the depth of the conviction concerning its overpowering meaningfulness, regardless of whether any attempt is made to unite this content with a divine Being, for otherwise it would not be possible to count Buddha and Spinoza as religious personalities. Accordingly, a religious person is devout in the sense that he has no doubt of the significance and loftiness of those superpersonal objects and goals which neither require nor are capable of rational foundation. They exist with the same necessity and matter-of-factness as he himself. In this sense religion is the age-old endeavor of mankind to become clearly and completely conscious of these values and goals and constantly to strengthen and extend their effect. If one conceives of religion and science according to these definitions then a conflict between them appears impossible. For science can only ascertain what is, but not what should be, and outside of its domain value judgments of all kinds remain necessary.
…...
A regiment of soldiers on parade is, according to some philosophers, a system.
From Selected Aphorisms from the Lyceum (1797-1800). As translated by Luis H. Gray in Kuno Francke and Isidore Singer (eds.), The German Classics: Masterpieces of German Literature Translated Into English (1913), Vol. 4, 176.
A scientist is a man who changes his beliefs according to reality; a theist is a man who changes reality to match his beliefs.
In Dave Lane, Isn’t Religion Weird? Quotations for Atheists (2008), 10, with no citation. If you know the primary source, please contact Webmaster, who has meanwhile only tentatively assumed that the quote comes from Volker Braun the German playwright (but has confirmed it is not from Volker Braun the physicist).
A vital phenomenon can only be regarded as explained if it has been proven that it appears as the result of the material components of living organisms interacting according to the laws which those same components follow in their interactions outside of living systems.
Gesammelte Schriften (1904), Vol. 3, 767. Trans. Paul F. Cranefield, 'The Organic Physics of 1847 and the Biophysics of Today', Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences, 1957, 12, 410.
A word is not a crystal, transparent and unchanged, it is the skin of a living thought and may vary greatly in color and content according to the circumstances and the time in which it is used.
In Towne v. Eisner (1918), 245 U.S. 425. As quoted in Richard A. Posner (ed.), The Essential Holmes: Selections from the Letters, Speeches, Judicial Opinions, and Other Writings of Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr. (1992), 287.
Absorbed in the special investigation, I paid no heed to the edifice which was meanwhile unconsciously building itself up. Having however completed the comparison of the fossil species in Paris, I wanted, for the sake of an easy revision of the same, to make a list according to their succession in geological formations, with a view of determining the characteristics more exactly and bringing them by their enumeration into bolder relief. What was my joy and surprise to find that the simplest enumeration of the fossil fishes according to their geological succession was also a complete statement of the natural relations of the families among themselves; that one might therefore read the genetic development of the whole class in the history of creation, the representation of the genera and species in the several families being therein determined; in one word, that the genetic succession of the fishes corresponds perfectly with their zoological classification, and with just that classification proposed by me.
Quoted in Elizabeth Cary Agassiz (ed.), Louis Agassiz: His Life and Correspondence (1885), Vol. I, 203-4.
According to astronomers, next week Wednesday will occur twice. They say such a thing happens only once every 60,000 years and although they don’t know why it occurs, they’re glad they have an extra day to figure it out.
In Napalm and Silly Putty (2002), 105.
According to Democritus, atoms had lost the qualities like colour, taste, etc., they only occupied space, but geometrical assertions about atoms were admissible and required no further analysis. In modern physics, atoms lose this last property, they possess geometrical qualities in no higher degree than colour, taste, etc. The atom of modern physics can only be symbolized by a partial differential equation in an abstract multidimensional space. Only the experiment of an observer forces the atom to indicate a position, a colour and a quantity of heat. All the qualities of the atom of modern physics are derived, it has no immediate and direct physical properties at all, i.e. every type of visual conception we might wish to design is, eo ipso, faulty. An understanding of 'the first order' is, I would almost say by definition, impossible for the world of atoms.
Philosophic Problems of Nuclear Science, trans. F. C. Hayes (1952), 38.
According to Gandhi, the seven sins are wealth without works, pleasure without conscience, knowledge without character, commerce without morality, science without humanity, worship without sacrifice, and politics without principle. Well, Hubert Humphrey may have sinned in the eyes of God, as we all do, but according to those definitions of Gandhi’s, it was Hubert Humphrey without sin.
Eulogy at funeral of Vice President Hubert Humphrey, St. Paul, Minnesota (16 Jan 1978). In Public Papers of the Presidents of the United States: Jimmy Carter (1978), Vol. 1, 82.
According to Herr Cook's observation, the inhabitants of New Guinea have something they set light to which burns up almost like gunpowder. They also put it into hollow staves, and from a distance you could believe they are shooting. But it does not produce so much as a bang. Presumably they are trying to imitate the Europeans. They have failed to realize its real purpose.
Aphorism 27 in Notebook D (1773-1775), as translated by R.J. Hollingdale in Aphorisms (1990). Reprinted as The Waste Books (2000), 48.
According to my derivative hypothesis, a change takes place first in the structure of the animal, and this, when sufficiently advanced, may lead to modifications of habits… . “Derivation” holds that every species changes, in time, by virtue of inherent tendencies thereto. “Natural Selection” holds that no such change can take place without the influence of altered external circumstances educing or selecting such change… . The hypothesis of “natural selection” totters on the extension of a conjectural condition, explanatory of extinction to the majority of organisms, and not known or observed to apply to the origin of any species.
In On the Anatomy of Vertebrates (1868), Vol. 3, 808.
According to my views, aiming at quantitative investigations, that is at establishing relations between measurements of phenomena, should take first place in the experimental practice of physics. By measurement to knowledge [door meten tot weten] I should like to write as a motto above the entrance to every physics laboratory.
'The Significance of Quantitative Research in Physics', Inaugural Address at the University of Leiden (1882). In Hendrik Casimir, Haphazard Reality: Half a Century of Science (1983), 160-1.
According to our ancient Buddhist texts, a thousand million solar systems make up a galaxy. … A thousand million of such galaxies form a supergalaxy. … A thousand million supergalaxies is collectively known as supergalaxy Number One. Again, a thousand million supergalaxy Number
Ones form a Supergalaxy Number Two. A thousand million supergalaxy Number Twos make up a supergalaxy Number Three, and of these, it is stated in the texts that there are a countless number in the universe.
In 'Reactions to Man’s Landing on the Moon Show Broad Variations in Opinions', The New York Times (21 Jul 1969), 6.
According to the Boshongo people of central Africa, in the beginning, there was only darkness, water, and the great god Bumba. One day Bumba, in pain from a stomach ache, vomited up the sun. The sun dried up some of the water, leaving land. Still in pain, Bumba vomited up the moon, the stars, and then some animals. The leopard, the crocodile, the turtle, and finally, man. This creation myth, like many others, tries to answer the questions we all ask. Why are we here? Where did we come from?
Lecture (1987), 'The Origin of the Universe', collected in Black Holes And Baby Universes And Other Essays (1993), 99.
According to the common law of nature, deficiency of power is supplied by duration of time.
'Geological Illustrations', Appendix to G. Cuvier, Essay on the Theory of the Earth, trans. R. Jameson (1827), 430.
According to the conclusion of Dr. Hutton, and of many other geologists, our continents are of definite antiquity, they have been peopled we know not how, and mankind are wholly unacquainted with their origin. According to my conclusions drawn from the same source, that of facts, our continents are of such small antiquity, that the memory of the revolution which gave them birth must still be preserved among men; and thus we are led to seek in the book of Genesis the record of the history of the human race from its origin. Can any object of importance superior to this be found throughout the circle of natural science?
An Elementary Treatise on Geology (1809), 82.
According to the estimate of a prominent advertising firm, above 90 per cent, of the earning capacity of the prominent nostrums is represented by their advertising. And all this advertising is based on the well-proven theory of the public's pitiable ignorance and gullibility in the vitally important matter of health.
'The Fundamental Fakes', Collier's Weekly (17 Feb 1906). Reprinted in The Great American Fraud (1907), 55.
According to the older view, for every single effect of a serum, there was a separate substance, or at least a particular chemical group... A normal serum contained as many different haemagglutinins as it agglutinated different cells. The situation was undoubtedly made much simpler if, to use the Ehrlich terminology... the separate haptophore groups can combine with an extremely large number of receptors in stepwise differing quantities as a stain does with different animal tissues, though not always with the same intensity. A normal serum would therefore visibly affect such a large number of different blood cells... not because it contained countless special substances, but because of the colloids of the serum, and therefore of the agglutinins by reason of their chemical constitution and the electrochemical properties resulting from it. That this manner of representation is a considerable simplification is clear; it also opens the way to direct experimental testing by the methods of structural chemistry.
'Die Theorien der Antikorperbildung ... ', Wiener klinische Wöchenschrift (1909), 22, 1623-1631. Trans. Pauline M. H. Mazumdar.
According to the theory of aerodynamics, as may be readily demonstrated through wind tunnel experiments, the bumblebee is unable to fly. This is because the size, weight and shape of his body in relation to the total wingspread make flying impossible. But the bumblebee, being ignorant of these scientific truths, goes ahead and flies anyway—and makes a little honey every day.
Sign in a General Motors Corporation factory. As quoted in Ralph L. Woods, The Businessman's
Book of Quotations (1951), 249-50. Cited in Suzy Platt (ed)., Respectfully Quoted: A Dictionary of Quotations (1989), 118.
According to their [Newton and his followers] doctrine, God Almighty wants to wind up his watch from time to time: otherwise it would cease to move. He had not, it seems, sufficient foresight to make it a perpetual motion. Nay, the machine of God's making, so imperfect, according to these gentlemen; that he is obliged to clean it now and then by an extraordinary concourse, and even to mend it, as clockmaker mends his work.
'Mr. Leibniz's First Paper' (1715). In H. G. Alexander (ed.), The Leibniz-Clarke Correspondence (1956), 11-2.
According to this view of the matter, there is nothing casual in the formation of Metamorphic Rocks. All strata, once buried deep enough, (and due TIME allowed!!!) must assume that state,—none can escape. All records of former worlds must ultimately perish.
Letter to Mr Murchison, In explanation of the views expressed in his previous letter to Mr Lyell, 15 Nov 1836. Quoted in the Appendix to Charles Babbage, The Ninth Bridgewater Treatise: A Fragment (1838), 240.
After all, we scientific workers … like women, are the victims of fashion: at one time we wear dissociated ions, at another electrons; and we are always loth to don rational clothing; some fixed belief we must have manufactured for us: we are high or low church, of this or that degree of nonconformity, according to the school in which we are brought up—but the agnostic is always rare of us and of late years the critic has been taboo.
'The Thirst of Salted Water or the Ions Overboard', Science Progress (1909), 3, 643.
After the discovery of spectral analysis no one trained in physics could doubt the problem of the atom would be solved when physicists had learned to understand the language of spectra. So manifold was the enormous amount of material that has been accumulated in sixty years of spectroscopic research that it seemed at first beyond the possibility of disentanglement. An almost greater enlightenment has resulted from the seven years of Röntgen spectroscopy, inasmuch as it has attacked the problem of the atom at its very root, and illuminates the interior. What we are nowadays hearing of the language of spectra is a true 'music of the spheres' in order and harmony that becomes ever more perfect in spite of the manifold variety. The theory of spectral lines will bear the name of Bohr for all time. But yet another name will be permanently associated with it, that of Planck. All integral laws of spectral lines and of atomic theory spring originally from the quantum theory. It is the mysterious organon on which Nature plays her music of the spectra, and according to the rhythm of which she regulates the structure of the atoms and nuclei.
Atombau und Spektrallinien (1919), viii, Atomic Structure and Spectral Lines, trans. Henry L. Brose (1923), viii.
All things began in Order, so shall they end, and so shall they begin again, according to the Ordainer of Order, and the mystical mathematicks of the City of Heaven.
In 'Garden of Cyrus', Religio Medici and Other Writings (1909), 229.
An experiment in nature, like a text in the Bible, is capable of different interpretations, according to the preconceptions of the interpreter.
Physiological Disquisitions (1781), 148.
An induction shock results in a contraction or fails to do so according to its strength; if it does so at all, it produces in the muscle at that time the maximal contraction that can result from stimuli of any strength.
Über die Eigentümlichkeiten der Reizbarkeit welche die Muskelfasern des Herzen zeigen', Ber. süchs. Akad. Wiss., Math.-nat Klasse, 1871, 23, 652-689. Trans. Edwin Clarke and C. D. O'Malley, The Human Brain and Spinal Cord (1968), 218.
An irrefutable proof that such single-celled primaeval animals really existed as the direct ancestors of Man, is furnished according to the fundamental law of biogeny by the fact that the human egg is nothing more than a simple cell.
Natürlche Schöpfungsgeschichte, trans. E. R. Lankester, The History of Creation (1892), Vol. 2, 381.
Anaximander son of Praxiades, of Miletus: he said that the principle and element is the Indefinite, not distinguishing air or water or anything else. … he was the first to discover a gnomon, and he set one up on the Sundials (?) in Sparta, according to Favorinus in his Universal History, to mark solstices and equinoxes; and he also constructed hour indicators. He was the first to draw an outline of earth and sea, but also constructed a [celestial] globe. Of his opinions he made a summary exposition, which I suppose Apollodorus the Athenian also encountered. Apollodorus says in his Chronicles that Anaximander was sixty-four years old in the year of the fifty-eighth Olympiad [547/6 B.C.], and that he died shortly afterwards (having been near his prime approximately during the time of Polycrates, tyrant of Samos).
Diogenes Laërtius II, 1-2. In G.S. Kirk, J.E. Raven and M. Schofield (eds), The Presocratic Philosophers: A Critical History with a Selection of Texts (1957), 99. The editors of this translation note that Anaximander may have introduced the gnomon into Greece, but he did not discover it—the Babylonians used it earlier, and the celestial sphere, and the twelve parts of the day.
Anaximenes son of Eurystratus, of Miletus, was a pupil of Anaximander; some say he was also a pupil of Parmenides. He said that the material principle was air and the infinite; and that the stars move, not under the earth, but round it. He used simple and economical Ionic speech. He was active, according to what Apollodorus says, around the time of the capture of Sardis, and died in the 63rd Olympiad.
Diogenes Laertius 2.3. In G. S. Kirk, J. E. Raven and M. Schofield (eds), The Presocratic Philosophers: A Critical History with a Selection of Texts(1983), p. 143.
And God said, “Let the earth put forth vegetation, plants yielding seed, and fruit trees bearing fruit in which is their seed, each according to its kind.” And God saw that it was good. And there was evening and there was morning, a third day.
— Bible
(circa 725 B.C.)
And of every living thing of all flesh, you shall bring two of every sort into the ark, to keep them alive with you; they shall be male and female. Of the birds according to their kinds, and of the animals according to their kinds, of every creeping thing of the ground according to its kind.
— Bible
(circa 725 B.C.)
Another diversity of Methods is according to the subject or matter which is handled; for there is a great difference in delivery of the Mathematics, which are the most abstracted of knowledges, and Policy, which is the most immersed…, yet we see how that opinion, besides the weakness of it, hath been of ill desert towards learning, as that which taketh the way to reduce learning to certain empty and barren generalities; being but the very husks and shells of sciences, all the kernel being forced out and expulsed with the torture and press of the method.
Advancement of Learning, Book 2. In James Spedding, The Works of Francis Bacon (1863), Vol. 6, 292-293. Peter Pešić, explains that 'By Mathematics, he had in mind a sterile and rigid scheme of logical classifications, called dichotomies in his time,' inLabyrinth: A Search for the Hidden Meaning of Science (2001), 73.
Archeus, the Workman and Governour of generation, doth cloath himself presently with a bodily cloathing: For in things soulified he walketh thorow all the Dens and retiring places of his Seed, and begins to transform the matter, according to the perfect act of his own Image.
Oriatrike: Or, Physick Refined, trans. John Chandler (1662), 35.
Archimedes … had stated that given the force, any given weight might be moved, and even boasted, we are told, relying on the strength of demonstration, that if there were another earth, by going into it he could remove this. Hiero being struck with amazement at this, and entreating him to make good this problem by actual experiment, and show some great weight moved by a small engine, he fixed accordingly upon a ship of burden out of the king’s arsenal, which could not be drawn out of the dock without great labor and many men; and, loading her with many passengers and a full freight, sitting himself the while far off with no great endeavor, but only holding the head of the pulley in his hand and drawing the cords by degrees, he drew the ship in a straight line, as smoothly and evenly, as if she had been in the sea. The king, astonished at this, and convinced of the power of the art, prevailed upon Archimedes to make him engines accommodated to all the purposes, offensive and defensive, of a siege. … the apparatus was, in most opportune time, ready at hand for the Syracusans, and with it also the engineer himself.
— Plutarch
In John Dryden (trans.), Life of Marcellus.
As mineralogy constitutes a part of chemistry, it is clear that this arrangement [of minerals] must derive its principles from chemistry. The most perfect mode of arrangement would certainly be to allow bodies to follow each other according to the order of their electro-chemical properties, from the most electro-negative, oxygen, to the most electro-positive, potassium; and to place every compound body according to its most electro-positive ingredient.
An Attempt to Establish a Pure Scientific System of Mineralogy (1814), trans. J. Black, 48.
Bacteria are highly adaptable. They frequently change both morphologically and functionally. Their virulence is also an essentially fluctuating property, that increases or diminishes according to the conditions to which the pathogenic organism is subjected.
In Studies in Immunity (1909), 1.
Because intelligence is our own most distinctive feature, we may incline to ascribe superior intelligence to the basic primate plan, or to the basic plan of the mammals in general, but this point requires some careful consideration. There is no question at all that most mammals of today are more intelligent than most reptiles of today. I am not going to try to define intelligence or to argue with those who deny thought or consciousness to any animal except man. It seems both common and scientific sense to admit that ability to learn, modification of action according to the situation, and other observable elements of behavior in animals reflect their degrees of intelligence and permit us, if only roughly, to compare these degrees. In spite of all difficulties and all the qualifications with which the expert (quite properly) hedges his conclusions, it also seems sensible to conclude that by and large an animal is likely to be more intelligent if it has a larger brain at a given body size and especially if its brain shows greater development of those areas and structures best developed in our own brains. After all, we know we are intelligent, even though we wish we were more so.
In The Meaning of Evolution: A Study of the History of Life and of its Significance for Man (1949), 78.
But when you come right down to it, the reason that we did this job is because it was an organic necessity. If you are a scientist you cannot stop such a thing. If you are a scientist you believe that it is good to find out how the world works; that it is good to find out what the realities are; that it is good to turn over to mankind at large the greatest possible power to control the world and to deal with it according to its lights and values.
Regarding the atomic bomb project.
Regarding the atomic bomb project.
From speech at Los Alamos (17 Oct 1945). Quoted in David C. Cassidy, J. Robert Oppenheimer and the American Century (2009), 214.
Coterminous with space and coeval with time is the kingdom of Mathematics; within this range her dominion is supreme; otherwise than according to her order nothing can exist; in contradiction to her laws nothing takes place. On her mysterious scroll is to be found written for those who can read it that which has been, that which is, and that which is to come.
From Presidential Address (Aug 1878) to the British Association, Dublin, published in the Report of the 48th Meeting of the British Association for the Advancement of Science (1878), 31.
Deaths, births, and marriages, considering how much they are separately dependent on the freedom of the human will, should seem to be subject to no law according to which any calculation could be made beforehand of their amount; and yet the yearly registers of these events in great countries prove that they go on with as much conformity to the laws of nature as the oscillations of the weather.
'Idea of a Universal history on a Cosmo-Political Plan' (1784). As translated by Thomas De Quinsey in The London Magazine (Oct 1824), 10, 385. Reprinted in 1859 by De Quincey in Vol. 8 of his Collective Edition of his writings.
Democritus sometimes does away with what appears to the senses, and says that none of these appears according to truth but only according to opinion: the truth in real things is that there are atoms and void. “By convention sweet”, he says, “by convention bitter, by convention hot, by convention cold, by convention colour: but in reality atoms and void.”
Against the Professors, 7, 135. In G. S. Kirk, J. E. Raven and M. Schofield (eds.), The Presocratic Philosophers: A Critical History with a Selection of Texts (1983), 410.
Disease is not something personal and special, but only a manifestation of life under modified conditions, operating according to the same laws as apply to the living body at all times, from the first moment until death.
In Ian F. McNeely, Medicine on a Grand Scale: Rudolf Virchow, Liberalism, and the Public Health (2002), 26.
During the time of the Deluge, whilst the Water was out upon, and covered the Terrestrial Globe, … all Fossils whatever that had before obtained any Solidity, were totally dissolved, and their constituent Corpuscles all disjoyned, their Cohesion perfectly ceasing … [A]nd, to be short, all Bodies whatsoever that were either upon the Earth, or that constituted the Mass of it, if not quite down to the Abyss, yet at least to the greatest depth we ever dig: I say all these were assumed up promiscuously into the Water, and sustained in it, in such a manner that the Water, and Bodies in it, together made up one common confused Mass. That at length all the Mass that was thus borne up in the Water, was again precipitated and subsided towards the bottom. That this subsidence happened generally, and as near as possibly could be expected in so great a Confusion, according to the laws of Gravity.
In An Essay Toward A Natural History of the Earth (1695), 74-75.
Euclidean mathematics assumes the completeness and invariability of mathematical forms; these forms it describes with appropriate accuracy and enumerates their inherent and related properties with perfect clearness, order, and completeness, that is, Euclidean mathematics operates on forms after the manner that anatomy operates on the dead body and its members. On the other hand, the mathematics of variable magnitudes—function theory or analysis—considers mathematical forms in their genesis. By writing the equation of the parabola, we express its law of generation, the law according to which the variable point moves. The path, produced before the eyes of the student by a point moving in accordance to this law, is the parabola.
If, then, Euclidean mathematics treats space and number forms after the manner in which anatomy treats the dead body, modern mathematics deals, as it were, with the living body, with growing and changing forms, and thus furnishes an insight, not only into nature as she is and appears, but also into nature as she generates and creates,—reveals her transition steps and in so doing creates a mind for and understanding of the laws of becoming. Thus modern mathematics bears the same relation to Euclidean mathematics that physiology or biology … bears to anatomy.
If, then, Euclidean mathematics treats space and number forms after the manner in which anatomy treats the dead body, modern mathematics deals, as it were, with the living body, with growing and changing forms, and thus furnishes an insight, not only into nature as she is and appears, but also into nature as she generates and creates,—reveals her transition steps and in so doing creates a mind for and understanding of the laws of becoming. Thus modern mathematics bears the same relation to Euclidean mathematics that physiology or biology … bears to anatomy.
In Die Mathematik die Fackelträgerin einer neuen Zeit (1889), 38. As translated in Robert Édouard Moritz, Memorabilia Mathematica; Or, The Philomath’s Quotation-book (1914), 112-113.
Every arsenate has its corresponding phosphate, composed according to the same proportions, combined with the same amount of water of crystallization, and endowed with the same physical properties: in fact, the two series of salts differ in no respect, except that the radical of the acid in one series in phosphorus, while in the other it is arsenic.
The experimental clue he used forming his law of isomerism. Originally published in 'Om Förhållandet emellan chemiska sammansättningen och krystallformen hos Arseniksyrade och Phosphorsyrade Salter', (On the Relation between the Chemical Composition and Crystal Form of Salts of Arsenic and Phosphoric Acids), Kungliga Svenska vetenskapsakademiens handlingar (1821), 4. Translation as shown in Joseph William Mellor, A Comprehensive Treatise on Inorganic and Theoretical Chemistry (1922), Vol. 1, 652. A very similar translation (“the same physical properties” is replaced with “nearly equal solubilities in water and acids”) is in F. Szabadváry article on 'Eilhard Mitscherlich' in Charles Coulston Gillispie (ed.), Dictionary of Scientific Biography (1974), Vol. 9, 424; perhaps from J.R. Partington, A History of Chemistry, Vol. 4 (1964), 210.

Every chemical substance, whether natural or artificial, falls into one of two major categories, according to the spatial characteristic of its form. The distinction is between those substances that have a plane of symmetry and those that do not. The former belong to the mineral, the latter to the living world.
Pasteur Vallery-Radot (ed.), Oeuvres de Pasteur (1922-1939), Vol. I, 331. Quoted in Patrice Debré, Louis Pasteur, trans. Elborg Forster (1994), 261.
Every gambler stakes a certainty to gain an uncertainty, and yet he stakes a finite certainty against a finite uncertainty without acting unreasonably. … The uncertainty of gain is proportioned to the certainty of the stake, according to the proportion of chances of gain and loss, and if therefore there are as many chances on one side as on the other, the game is even.
In Blaise Pascal and C. Kegan Paul (trans.), 'Of The Need of Seeking Truth', The Thought of Blaise Pascal: Translated from the Text of M. Auguste Molinier (1905), 98.
Everything is made of atoms ... Everything that animals do, atoms do. ... There is nothing that living things do that cannot be understood from the point of view that they are made of atoms acting according to the laws of physics.
In The Feynman Lectures (1963), 8.
Exper. I. I made a small hole in a window-shutter, and covered it with a piece of thick paper, which I perforated with a fine needle. For greater convenience of observation I placed a small looking-glass without the window-shutter, in such a position as to reflect the sun's light, in a direction nearly horizontal, upon the opposite wall, and to cause the cone of diverging light to pass over a table on which were several little screens of card-paper. I brought into the sunbeam a slip of card, about one-thirtieth of an inch in breadth, and observed its shadow, either on the wall or on other cards held at different distances. Besides the fringes of colour on each side of the shadow, the shadow itself was divided by similar parallel fringes, of smaller dimensions, differing in number, according to the distance at which the shadow was observed, but leaving the middle of the shadow always white. Now these fringes were the joint effects of the portions of light passing on each side of the slip of card and inflected, or rather diffracted, into the shadow. For, a little screen being placed a few inches from the card, so as to receive either edge of the shadow on its margin, all the fringes which had before been observed in the shadow on the wall, immediately disappeared, although the light inflected on the other side was allowed to retain its course, and although this light must have undergone any modification that the proximity of the other edge of the slip of card might have been capable of occasioning... Nor was it for want of a sufficient intensity of light that one of the two portions was incapable of producing the fringes alone; for when they were both uninterrupted, the lines appeared, even if the intensity was reduced to one-tenth or one-twentieth.
'Experiments and Calculations Relative to Physical Optics' (read in 1803), Philosophical Transactions (1804), 94, 2-3.
For the little that one has reflected on the origin of our knowledge, it is easy to perceive that we can acquire it only by means of comparison. That which is absolutely incomparable is wholly incomprehensible. God is the only example that we could give here. He cannot be comprehended, because he cannot be compared. But all which is susceptible of comparison, everything that we can perceive by different aspects, all that we can consider relatively, can always be judged according to our knowledge.
'Histoire naturelle de l'Homme', Histoire Naturelle, Générale et Particulière, Avec la Description du Cabinet du Roi (1749), Vol. 2, 431. Trans. Phillip R. Sloan.
For the philosopher, order is the entirety of repetitions manifested, in the form of types or of laws, by perceived objects. Order is an intelligible relation. For the biologist, order is a sequence in space and time. However, according to Plato, all things arise out of their opposites. Order was born of the original disorder, and the long evolution responsible for the present biological order necessarily had to engender disorder.
An organism is a molecular society, and biological order is a kind of social order. Social order is opposed to revolution, which is an abrupt change of order, and to anarchy, which is the absence of order.
I am presenting here today both revolution and anarchy, for which I am fortunately not the only one responsible. However, anarchy cannot survive and prosper except in an ordered society, and revolution becomes sooner or later the new order. Viruses have not failed to follow the general law. They are strict parasites which, born of disorder, have created a very remarkable new order to ensure their own perpetuation.
An organism is a molecular society, and biological order is a kind of social order. Social order is opposed to revolution, which is an abrupt change of order, and to anarchy, which is the absence of order.
I am presenting here today both revolution and anarchy, for which I am fortunately not the only one responsible. However, anarchy cannot survive and prosper except in an ordered society, and revolution becomes sooner or later the new order. Viruses have not failed to follow the general law. They are strict parasites which, born of disorder, have created a very remarkable new order to ensure their own perpetuation.
'Interaction Among Virus, Cell, and Organism', Nobel Lecture (11 Dec 1965). In Nobel Lectures: Physiology or Medicine 1963-1970 (1972), 174.
For, Mathematical Demonstrations being built upon the impregnable Foundations of Geometry and Arithmetick, are the only Truths, that can sink into the Mind of Man, void of all Uncertainty; and all other Discourses participate more or less of Truth, according as their Subjects are more or less capable of Mathematical Demonstration.
Inaugural lecture of Christopher Wren in his chair of astronomy at Gresham College (1657). From Parentelia (1741, 1951), 200-201.
From common salt are obtained chemically as primary derivatives chlorine—both a war gas and a means of purifying water; and 'caustic soda.' … [O]n the chlorine side there is obtained chloride of lime, (a bleaching powder and a disinfectant), chloroform (an anesthetic), phosgene (a frightful ware gas), chloroacetophenone (another war gas), and an indigo and a yellow dye. [O]n the soda side we get metallic sodium, from which are derived sodium cyanide (a disinfectant), two medicines with [long] names, another war gas, and a beautiful violet dye. Thus, from a healthful, preservative condiment come things useful and hurtful—according to the intent or purpose.
The Homiletic Review, Vol. 83-84 (1922), Vol. 83, 209.
From the war of nature, from famine and death, the most exalted object which we are capable of conceiving, namely, the production of the higher animals, directly follows. There is grandeur in this view of life, with its several powers, having been originally breathed into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonderful have been, and are being, evolved.
Concluding paragraph in The Origin of Species (1859), 490. In the second edition, Darwin changed “breathed” to “breathed by the Creator”.
Give me the liberty to know, to utter, and to argue freely according to conscience, above all liberties.
In Areopagitica: A speech of Mr John Milton for the Liberty of Unlicenced printing to the Parliament of England (23 Nov 1644), 35.
Half a century ago Oswald (1910) distinguished classicists and romanticists among the scientific investigators: the former being inclined to design schemes and to use consistently the deductions from working hypotheses; the latter being more fit for intuitive discoveries of functional relations between phenomena and therefore more able to open up new fields of study. Examples of both character types are Werner and Hutton. Werner was a real classicist. At the end of the eighteenth century he postulated the theory of “neptunism,” according to which all rocks including granites, were deposited in primeval seas. It was an artificial scheme, but, as a classification system, it worked quite satisfactorily at the time. Hutton, his contemporary and opponent, was more a romanticist. His concept of “plutonism” supposed continually recurrent circuits of matter, which like gigantic paddle wheels raise material from various depths of the earth and carry it off again. This is a very flexible system which opens the mind to accept the possible occurrence in the course of time of a great variety of interrelated plutonic and tectonic processes.
In 'The Scientific Character of Geology', The Journal of Geology (Jul 1961), 69, No. 4, 456-7.
He who would know what geometry is, must venture boldly into its depths and learn to think and feel as a geometer. I believe that it is impossible to do this, and to study geometry as it admits of being studied and am conscious it can be taught, without finding the reason invigorated, the invention quickened, the sentiment of the orderly and beautiful awakened and enhanced, and reverence for truth, the foundation of all integrity of character, converted into a fixed principle of the mental and moral constitution, according to the old and expressive adage “abeunt studia in mores”.
In 'A Probationary Lecture on Geometry, in Collected Mathematical Papers (1908), Vol. 2, 9. [The Latin phrase, “abeunt studia in mores” translates as “studies pass on into character”. —Webmaster]
HEART, n. An automatic, muscular blood- pump. Figuratively, this useful organ is said to be the seat of emotions and sentiments—a very pretty fancy which, however, is nothing but a survival of a once universal belief. It is now known that the sentiments and emotions reside in the stomach, being evolved from food by chemical action of the gastric fluid. The exact process by which a beefsteak becomes a feeling—tender or not, according to the age of the animal from which it was cut; the successive stages of elaboration through which a caviar sandwich is transmuted to a quaint fancy and reappears as a pungent epigram; the marvelous functional methods of converting a hard-boiled egg into religious contrition, or a cream-puff into a sigh of sensibility—these things have been patiently ascertained by M. Pasteur, and by him expounded with convincing lucidity.
The Collected Works of Ambrose Bierce (1911), Vol. 7, The Devil's Dictionary, 133-134.
Heraclitus son of Bloson (or, according to some, of Herakon) of Ephesus. This man was at his prime in the 69th Olympiad. He grew up to be exceptionally haughty and supercilious, as is clear also from his book, in which he says: “Learning of many things does not teach intelligence; if so it would have taught Hesiod and Pythagoras, and again Xenophanes and Hecataeus.” … Finally he became a misanthrope, withdrew from the world, and lived in the mountains feeding on grasses and plants. However, having fallen in this way into a dropsy he came down to town and asked the doctors in a riddle if they could make a drought out of rainy weather. When they did not understand he buried himself in a cow-stall, expecting that the dropsy would be evaporated off by the heat of the manure; but even so he failed to effect anything, and ended his life at the age of sixty.
Diogenes Laertius 9.1. In G. S. Kirk, E. Raven, and M. Schofield (eds.), The Presocratic philosophers: A Critical History with a Selection of Texts (1983), 181.
Human nature is not a machine to be built after a model, and set to do exactly the work prescribed for it, but a tree, which requires to grow and develop itself on all sides, according to the tendency of the inward forces which make it a living thing.
In 'Elements of Well-Being', On Liberty (1859), 107.
I am credited with being one of the hardest workers and perhaps I am, if thought is the equivalent of labour, for I have devoted to it almost all of my waking hours. But if work is interpreted to be a definite performance in a specified time according to a rigid rule, then I may be the worst of idlers. Every effort under compulsion demands a sacrifice of life-energy. I never paid such a price. On the contrary, I have thrived on my thoughts.
In 'My Early Life', My Inventions: And Other Writings (2016), 1. Originally published in serial form in Part 1, 'My Early Life' in the series of articles, 'My Inventions', Electrical Experimenter magazine (1919).
I am particularly concerned to determine the probability of causes and results, as exhibited in events that occur in large numbers, and to investigate the laws according to which that probability approaches a limit in proportion to the repetition of events. That investigation deserves the attention of mathematicians because of the analysis required. It is primarily there that the approximation of formulas that are functions of large numbers has its most important applications. The investigation will benefit observers in identifying the mean to be chosen among the results of their observations and the probability of the errors still to be apprehended. Lastly, the investigation is one that deserves the attention of philosophers in showing how in the final analysis there is a regularity underlying the very things that seem to us to pertain entirely to chance, and in unveiling the hidden but constant causes on which that regularity depends. It is on the regularity of the main outcomes of events taken in large numbers that various institutions depend, such as annuities, tontines, and insurance policies. Questions about those subjects, as well as about inoculation with vaccine and decisions of electoral assemblies, present no further difficulty in the light of my theory. I limit myself here to resolving the most general of them, but the importance of these concerns in civil life, the moral considerations that complicate them, and the voluminous data that they presuppose require a separate work.
Philosophical Essay on Probabilities (1825), trans. Andrew I. Dale (1995), Introduction.
I am the most travelled of all my contemporaries; I have extended my field of enquiry wider than anybody else, I have seen more countries and climes, and have heard more speeches of learned men. No one has surpassed me in the composition of lines, according to demonstration, not even the Egyptian knotters of ropes, or geometers.
In Alan L. Mackay, A Dictionary of Scientific Quotations (1992, 1994), 71.
I attained a triumph so complete that it is now rare to meet an American with marks of small pox on his face... Benefits are valuable according to their duration and extent, like the showers from heaven, but the benign remedy Vaccination saves millions of lives every century, like the blessing of the sun, universal and everlasting.
(Remark made near the end of his life.)
(Remark made near the end of his life.)
I can remember … starting to gather all sorts of things like rocks and beetles when I was about nine years old. There was no parental encouragement—nor discouragement either—nor any outside influence that I can remember in these early stages. By about the age of twelve, I had settled pretty definitely on butterflies, largely I think because the rocks around my home were limited to limestone, while the butterflies were varied, exciting, and fairly easy to preserve with household moth-balls. … I was fourteen, I remember, when … I decided to be scientific, caught in some net of emulation, and resolutely threw away all of my “childish” specimens, mounted haphazard on “common pins” and without “proper labels.” The purge cost me a great inward struggle, still one of my most vivid memories, and must have been forced by a conflict between a love of my specimens and a love for orderliness, for having everything just exactly right according to what happened to be my current standards.
In The Nature of Natural History (1950, 1990), 255.
I have come to the conclusion that mankind consume twice too much food. According to my computation, I have eaten and drunk, between my tenth and seventieth year, forty-four horse-wagon loads more than was good for me.
Quoted in Lydia Maria Francis Child, 'Hints About Health', Looking Toward Sunset (1891), 428.
I have satisfied myself that the [cosmic] rays are not generated by the formation of new matter in space, a process which would be like water running up a hill. Nor do they come to any appreciable amount from the stars. According to my investigations the sun emits a radiation of such penetrative power that it is virtually impossible to absorb it in lead or other substances. ... This ray, which I call the primary solar ray, gives rise to a secondary radiation by impact against the cosmic dust scattered through space. It is the secondary radiation which now is commonly called the cosmic ray, and comes, of course, equally from all directions in space. [The article continues: The phenomena of radioactivity are not the result of forces within the radioactive substances but are caused by this ray emitted by the sun. If radium could be screened effectively against this ray it would cease to be radioactive, he said.]
Quoted in 'Tesla, 75, Predicts New Power Source', New York Times (5 Jul 1931), Section 2, 1.
I have therefore tried to show the tendency displayed throughout history, by the most profound investigators, to pass from the world of the senses to a world where vision becomes spiritual, where principles are elaborated, and from which the explorer emerges with conceptions and conclusions, to be approved or rejected according as they coincide with sensible things.
Heat, A Mode of Motion (1880, 1915), 6th ed., viii.
I here present the reader with a new sign which I have discovered for detecting diseases of the chest. This consists in percussion of the human thorax, whereby, according to the character of the particular sounds then elicited, an opinion is formed of the internal state of that cavity.
New Invention by Means of Percussing the Human Thorax for Detecting Signs of Obscure Disease of the Interior of the Chest, Inventum novum ex percussione (31 Dec 1761).
I hope that in 50 years we will know the answer to this challenging question: are the laws of physics unique and was our big bang the only one? … According to some speculations the number of distinct varieties of space—each the arena for a universe with its own laws—could exceed the total number of atoms in all the galaxies we see. … So do we live in the aftermath of one big bang among many, just as our solar system is merely one of many planetary systems in our galaxy? (2006)
In 'Martin Rees Forecasts the Future', New Scientist (18 Nov 2006), No. 2578.
I remember my first look at the great treatise of Maxwell’s when I was a young man… I saw that it was great, greater and greatest, with prodigious possibilities in its power… I was determined to master the book and set to work. I was very ignorant. I had no knowledge of mathematical analysis (having learned only school algebra and trigonometry which I had largely forgotten) and thus my work was laid out for me. It took me several years before I could understand as much as I possibly could. Then I set Maxwell aside and followed my own course. And I progressed much more quickly… It will be understood that I preach the gospel according to my interpretation of Maxwell.
From translations of a letter (24 Feb 1918), cited in Paul J. Nahin, Oliver Heaviside: The Life, Work, and Times of an Electrical Genius of the Victorian Age (2002), 24. Nahin footnotes that the words are not verbatim, but are the result of two translations. Heaviside's original letter in English was quoted, translated in to French by J. Bethenode, for the obituary he wrote, "Oliver Heaviside", in Annales des Posies Telegraphs (1925), 14, 521-538. The quote was retranslated back to English in Nadin's book. Bethenode footnoted that he made the original translation "as literally as possible in order not to change the meaning." Nadin assures that the retranslation was done likewise. Heaviside studyied Maxwell's two-volume Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism.
I require a term to express those bodies which can pass to the electrodes, or, as they are usually called, the poles. Substances are frequently spoken of as being electro-negative, or electro-positive, according as they go under the supposed influence of a direct attraction to the positive or negative pole. But these terms are much too significant for the use to which I should have to put them; for though the meanings are perhaps right, they are only hypothetical, and may be wrong; and then, through a very imperceptible, but still very dangerous, because continual, influence, they do great injury to science, by contracting and limiting the habitual view of those engaged in pursuing it. I propose to distinguish these bodies by calling those anions which go to the anode of the decomposing body; and those passing to the cathode, cations; and when I have occasion to speak of these together, I shall call them ions.
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1834, 124, 79.
I saw a horrible brown heap on the floor in the corner, which, but for previous experience in this dismal wise, I might not have suspected to be “the bed.” There was something thrown upon it and I asked what it was. “’Tis the poor craythur that stays here, sur; and ’tis very bad she is, ’tis very bad she’s been this long time, and ’tis better she’ll never be, and ’tis slape she doos all day, and ’tis wake she doos all night, and ‘tis the lead, Sur.” “The what?” “The lead, Sur. Sure, ’tis the lead-mills, where women gets took on at eighteen pence a day, Sur, when they makes application early enough, and is lucky and wanted, and ’tis lead-pisoned she is, Sur, and some of them gits lead-pisoned soon and some of them gets lead-pisoned later, and some but not many, niver, and ’tis all according to the constitooshun, Sur, and some constitooshuns is strong, and some is weak, and her constitooshun is lead-pisoned, bad as can be, Sur, and her brain is coming out at her ear, and it hurts her dreadful, and that’s what it is and niver no more and niver so less, Sur.”
In 'New Uncommercial Samples: A Small Star in the East', All the Year Round (19 Dec 1868), New Series, No. 3, 62.
I submit a body of facts which cannot be invalidated. My opinions may be doubted, denied, or approved, according as they conflict or agree with the opinions of each individual who may read them; but their worth will be best determined by the foundation on which they rest—the incontrovertible facts.
Experiments and Observations on the Gastric Juice, and the Physiology of Digestion (1833), Preface.
I think a strong claim can be made that the process of scientific discovery may be regarded as a form of art. This is best seen in the theoretical aspects of Physical Science. The mathematical theorist builds up on certain assumptions and according to well understood logical rules, step by step, a stately edifice, while his imaginative power brings out clearly the hidden relations between its parts. A well constructed theory is in some respects undoubtedly an artistic production. A fine example is the famous Kinetic Theory of Maxwell. ... The theory of relativity by Einstein, quite apart from any question of its validity, cannot but be regarded as a magnificent work of art.
Responding to the toast, 'Science!' at the Royal Academy of the Arts in 1932.)
Responding to the toast, 'Science!' at the Royal Academy of the Arts in 1932.)
Quoted in Lawrence Badash, 'Ernest Rutherford and Theoretical Physics,' in Robert Kargon and Peter Achinstein (eds.) Kelvin's Baltimore Lectures and Modern Theoretical Physics: Historical and Philosophical Perspectives (1987), 352.
I think I may fairly make two postulata. First, That food is necessary to the existence of man. Secondly, That the passion between the sexes is necessary and will remain nearly in its present state. These two laws ever since we have had any knowledge of mankind, appear to have been fixed laws of our nature; and, as we have not hitherto seen any alteration in them, we have no right to conclude that they will ever cease to be what they are now, without an immediate act of power in that Being who first arranged the system of the universe; and for the advantage of his creatures, still executes, according to fixed laws, all its various operations.
First 'Essay on the Principle of Population' (1798), reprinted in Parallel Chapters from the First and Second editions of An Essay on the Principle of Population (1895), 6.
I told him that for a modern scientist, practicing experimental research, the least that could be said, is that we do not know. But I felt that such a negative answer was only part of the truth. I told him that in this universe in which we live, unbounded in space, infinite in stored energy and, who knows, unlimited in time, the adequate and positive answer, according to my belief, is that this universe may, also, possess infinite potentialities.
Nobel Lecture, The Coming Age of the Cell, 12 Dec 1974
I took a glass retort, capable of containing eight ounces of water, and distilled fuming spirit of nitre according to the usual method. In the beginning the acid passed over red, then it became colourless, and lastly again all red: no sooner did this happen, than I took away the receiver; and tied to the mouth of the retort a bladder emptied of air, which I had moistened in its inside with milk of lime lac calcis, (i.e. lime-water, containing more quicklime than water can dissolve) to prevent its being corroded by the acid. Then I continued the distillation, and the bladder gradually expanded. Here-upon I left every thing to cool, tied up the bladder, and took it off from the mouth of the retort.— I filled a ten-ounce glass with this air and put a small burning candle into it; when immediately the candle burnt with a large flame, of so vivid a light that it dazzled the eyes. I mixed one part of this air with three parts of air, wherein fire would not burn; and this mixture afforded air, in every respect familiar to the common sort. Since this air is absolutely necessary for the generation of fire, and makes about one-third of our common air, I shall henceforth, for shortness sake call it empyreal air, [literally fire-air] the air which is unserviceable for the fiery phenomenon, and which makes abut two-thirds of common air, I shall for the future call foul air [literally corrupted air].
Chemische Abhandlung von der Luft und dem Feuer (1777), Chemical Observations and Experiments on Air and Fire (1780), trans. J. R. Forster, 34-5.
I was led to the conclusion that at the most extreme dilutions all salts would consist of simple conducting molecules. But the conducting molecules are, according to the hypothesis of Clausius and Williamson, dissociated; hence at extreme dilutions all salt molecules are completely disassociated. The degree of dissociation can be simply found on this assumption by taking the ratio of the molecular conductivity of the solution in question to the molecular conductivity at the most extreme dilution.
Letter to Van’t Hoff, 13 April 1887. In J. R. Partington, A History of Chemistry (1961), Vol. 4, 678.
Iamblichus in his treatise On the Arithmetic of Nicomachus observes p. 47- “that certain numbers were called amicable by those who assimilated the virtues and elegant habits to numbers.” He adds, “that 284 and 220 are numbers of this kind; for the parts of each are generative of each other according to the nature of friendship, as was shown by Pythagoras. For some one asking him what a friend was, he answered, another I (ετεϑος εγω) which is demonstrated to take place in these numbers.” [“Friendly” thus: Each number is equal to the sum of the factors of the other.]
In Theoretic Arithmetic (1816), 122. (Factors of 284 are 1, 2, 4 ,71 and 142, which give the sum 220. Reciprocally, factors of 220 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 11 ,22, 44, 55 and 110, which give the sum 284.) Note: the expression “alter ego” is Latin for “the other I.”
Ideas, like ghosts (according to the common notion of a ghost), must be spoken to a little before they will explain themselves.
From Dealings With the Firm of Dombey and Son (1846), Vol. 1, 184.
If some race of quadrumanous animals, especially one of the most perfect of them, were to lose, by force of circumstances or some other cause, the habit of climbing trees and grasping the branches with its feet in the same way as with its hands, in order to hold on to them; and if the individuals of this race were forced for a series of generations to use their feet only for walking, and to give up using their hands like feet; there is no doubt, according to the observations detailed in the preceding chapter, that these quadrumanous animals would at length be transformed into bimanous, and that the thumbs on their feet would cease to be separated from the other digits, when they only used their feet for walking.
Philosophie Zoologique (1809), Vol. 1, 349, trans. Hugh Elliot (1914), 170.
If the Humours of the Eye by old Age decay, so as by shrinking to make the Cornea and Coat of the Crystalline Humour grow flatter than before, the Light will not be refracted enough, and for want of a sufficient Refraction will not converge to the bottom of the Eye but to some place beyond it, and by consequence paint in the bottom of the Eye a confused Picture, and according to the Indistinctuess of this Picture the Object will appear confused. This is the reason of the decay of sight in old Men, and shews why their Sight is mended by Spectacles. For those Convex glasses supply the defect of plumpness in the Eye, and by increasing the Refraction make the rays converge sooner, so as to convene distinctly at the bottom of the Eye if the Glass have a due degree of convexity. And the contrary happens in short-sighted Men whose Eyes are too plump. For the Refraction being now too great, the Rays converge and convene in the Eyes before they come at the bottom; and therefore the Picture made in the bottom and the Vision caused thereby will not be distinct, unless the Object be brought so near the Eye as that the place where the converging Rays convene may be removed to the bottom, or that the plumpness of the Eye be taken off and the Refractions diminished by a Concave-glass of a due degree of Concavity, or lastly that by Age the Eye grow flatter till it come to a due Figure: For short-sighted Men see remote Objects best in Old Age, and therefore they are accounted to have the most lasting Eyes.
Opticks (1704), Book 1, Part 1, Axiom VII, 10-11.
If the Weismann idea triumphs, it will be in a sense a triumph of fatalism; for, according to it, while we may indefinitely improve the forces of our education and surroundings, and this civilizing nurture will improve the individuals of each generation, its actual effects will not be cumulative as regards the race itself, but only as regards the environment of the race; each new generation must start de novo, receiving no increment of the moral and intellectual advance made during the lifetime of its predecessors. It would follow that one deep, almost instinctive motive for a higher life would be removed if the race were only superficially benefited by its nurture, and the only possible channel of actual improvement were in the selection of the fittest chains of race plasma.
'The Present Problem of Heredity', The Atlantic Monthly (1891), 57, 363.
If there is a lesson in our story it is that the manipulation, according to strictly self-consistent rules, of a set of symbols representing one single aspect of the phenomena may produce correct, verifiable predictions, and yet completely ignore all other aspects whose ensemble constitutes reality.
In 'Epilogue', The Sleepwalkers: A History of Man’s Changing Vision of the Universe (1959, 1968), 533.
If we lived on a planet where nothing ever changed, there would be little to do. There would be nothing to figure out. There would be no impetus for science. And if we lived in an unpredictable world, where things changed in random or very complex ways, we would not be able to figure things out. But we live in an in-between universe, where things change, but according to patterns, rules, or as we call them, laws of nature. If I throw a stick up in the air, it always falls down. If the sun sets in the west, it always rises again the next morning in the east. And so it becomes possible to figure things out. We can do science, and with it we can improve our lives.
Cosmos (1980, 1985), 32.
If we wish to give an account of the atomic constitution of the aromatic compounds, we are bound to explain the following facts:
1) All aromatic compounds, even the most simple, are relatively richer in carbon than the corresponding compounds in the class of fatty bodies.
2) Among the aromatic compounds, as well as among the fatty bodies, a large number of homologous substances exist.
3) The most simple aromatic compounds contain at least six atoms of carbon.
4) All the derivatives of aromatic substances exhibit a certain family likeness; they all belong to the group of 'Aromatic compounds'. In cases where more vigorous reactions take place, a portion of the carbon is often eliminated, but the chief product contains at least six atoms of carbon These facts justify the supposition that all aromatic compounds contain a common group, or, we may say, a common nucleus consisting of six atoms of carbon. Within this nucleus a more intimate combination of the carbon atoms takes place; they are more compactly placed together, and this is the cause of the aromatic bodies being relatively rich in carbon. Other carbon atoms can be joined to this nucleus in the same way, and according to the same law, as in the case of the group of fatty bodies, and in this way the existence of homologous compounds is explained.
1) All aromatic compounds, even the most simple, are relatively richer in carbon than the corresponding compounds in the class of fatty bodies.
2) Among the aromatic compounds, as well as among the fatty bodies, a large number of homologous substances exist.
3) The most simple aromatic compounds contain at least six atoms of carbon.
4) All the derivatives of aromatic substances exhibit a certain family likeness; they all belong to the group of 'Aromatic compounds'. In cases where more vigorous reactions take place, a portion of the carbon is often eliminated, but the chief product contains at least six atoms of carbon These facts justify the supposition that all aromatic compounds contain a common group, or, we may say, a common nucleus consisting of six atoms of carbon. Within this nucleus a more intimate combination of the carbon atoms takes place; they are more compactly placed together, and this is the cause of the aromatic bodies being relatively rich in carbon. Other carbon atoms can be joined to this nucleus in the same way, and according to the same law, as in the case of the group of fatty bodies, and in this way the existence of homologous compounds is explained.
Bulletin de la Societé Chimique de France (1865), 1, 98. Trans. W. H. Brock.
If, in the course of a thousand or two thousand years, science arrives at the necessity of renewing its points of view, that will not mean that science is a liar. Science cannot lie, for it’s always striving, according to the momentary state of knowledge, to deduce what is true. When it makes a mistake, it does so in good faith. It’s Christianity that’s the liar. It’s in perpetual conflict with itself.
In Adolf Hitler, Hugh Redwald Trevor-Roper, translated by Norman Cameron and R. H. Stevens, '14 October 1941', Secret Conversations (1941 - 1944) (1953), 51
In Man the brain presents an ascensive step in development, higher and more strongly marked than that by which the preceding subclass was distinguished from the one below it. Not only do the cerebral hemispheres overlap the olfactory lobes and cerebellum, but they extend in advance of the one, and further back than the other. Their posterior development is so marked, that anatomists have assigned to that part the character of a third lobe; it is peculiar to the genus Homo, and equally peculiar is the 'posterior horn of the lateral ventricle,' and the 'hippocampus minor,' which characterize the hind lobe of each hemisphere. The superficial grey matter of the cerebrum, through the number and depth of the convolutions, attains its maximum of extent in Man. Peculiar mental powers are associated with this highest form of brain, and their consequences wonderfully illustrate the value of the cerebral character; according to my estimate of which, I am led to regard the genus Homo, as not merely a representative of a distinct order, but of a distinct subclass of the Mammalia, for which I propose a name of 'ARCHENCEPHALA.'
'On the Characters, Principles of Division, and Primary Groups of the Class MAMMALIA' (1857), Journal of the Proceedings of the Linnean Society of London (1858), 2, 19-20.
In my understanding of God I start with certain firm beliefs. One is that the laws of nature are not broken. We do not, of course, know all these laws yet, but I believe that such laws exist. I do not, therefore, believe in the literal truth of some miracles which are featured in the Christian Scriptures, such as the Virgin Birth or water into wine. ... God works, I believe, within natural laws, and, according to natural laws, these things happen.
Essay 'Science Will Never Give Us the Answers to All Our Questions', collected in Henry Margenau, and Roy Abraham Varghese (eds.), Cosmos, Bios, Theos (1992), 66.
In order that the facts obtained by observation and experiment may be capable of being used in furtherance of our exact and solid knowledge, they must be apprehended and analysed according to some Conceptions which, applied for this purpose, give distinct and definite results, such as can be steadily taken hold of and reasoned from.
Philosophy of the Inductive Sciences (1840), Vol. 2, 205.
In the beginning God created Heaven and Earth … Which beginning of time, according to our Cronologie, fell upon the entrance of the night preceding the twenty third day of Octob. in the year of the Julian Calendar, 710 [or 4004 B.C.]. Upon the first day therefore of the world, or Octob. 23. being our Sunday, God, together with the highest Heaven, created the Angels. Then having finished, as it were, the roofe of this building, he fell in hand with the foundation of this wonderfull Fabrick of the World, he fashioned this lowermost Globe, consisting of the Deep, and of the Earth; all the Quire of Angels singing together and magnifying his name therefore … And when the Earth was void and without forme, and darknesse covered the face of the Deepe, on the very middle of the first day, the light was created; which God severing from the darknesses, called the one day, and the other night.
In 'Annals of the Old Testament', The Annals of the World (1658), excerpted in Louis A. Ruprecht, God Gardened East: A Gardener's Meditation on the Dynamics of Genesis (2008), 53-54.
Induction. The mental operation by which from a number of individual instances, we arrive at a general law. The process, according to Hamilton, is only logically valid when all the instances included in the law are enumerated. This being seldom, if ever, possible, the conclusion of an Induction is usually liable to more or less uncertainty, and Induction is therefore incapable of giving us necessary (general) truths.
Stated as narrative, not a direct quote, by his biographer W.H.S. Monck in 'Glossary of Philosophical Terms', appended in Sir William Hamilton (1881), 181.
Interestingly, according to modern astronomers, space is finite. This is a very comforting thought—particularly for people who can never remember where they have left things.
Side Effects (1981), 36.
It always bothers me that according to the laws as we understand them today, it takes a computing machine an infinite number of logical operations to figure out what goes on in no matter how tiny a region of space and no matter how tiny a region of time … I have often made the hypothesis that ultimately physics will not require a mathematical statement, that in the end the machinery will be revealed and the laws will turn out to be simple, like the chequer board with all its apparent complexities. But this speculation is of the same nature as those other people make—“I like it”,“I don't like it”—and it is not good to be too prejudiced about these things.
In The Character of Physical Law (1965, 2001), 57.
It appears, according to the reported facts, that the electric conflict is not restricted to the conducting wire, but that it has a rather extended sphere of activity around it … the nature of the circular action is such that movements that it produces take place in directions precisely contrary to the two extremities of a given diameter. Furthermore, it seems that the circular movement, combined with the progressive movement in the direction of the length of the conjunctive wire, should form a mode of action which is exerted as a helix around this wire as an axis.
Recherches sur l’identité des forces chimiques et électriques (1813), 248. In James R. Hofmann, André-Marie Ampère (1996), 231.
It has hitherto been a serious impediment to the progress of knowledge, that is in investigating the origin or causes of natural productions, recourse has generally been had to the examination, both by experiment and reasoning, of what might be rather than what is. The laws or processes of nature we have every reason to believe invariable. Their results from time to time vary, according to the combinations of influential circumstances; but the process remains the same. Like the poet or the painter, the chemist may, and no doubt often' does, create combinations which nature never produced; and the possibility of such and such processes giving rise to such and such results, is no proof whatever that they were ever in natural operation.
Considerations on Volcanoes (1825), 243.
It is clear, from these considerations, that the three methods of classifying mankind—that according to physical characters, according to language, and according to culture—all reflect the historical development of races from different standpoints; and that the results of the three classifications are not comparable, because the historical facts do not affect the three classes of phenomena equally. A consideration of all these classes of facts is needed when we endeavour to reconstruct the early history of the races of mankind.
'Summary of the Work of the Committee in British Columbia', Report of the Sixty-Eighth Meeting of the British Association for the Advancement of Science, 1899, 670.
It is difficult even to attach a precise meaning to the term “scientific truth.” So different is the meaning of the word “truth” according to whether we are dealing with a fact of experience, a mathematical proposition or a scientific theory. “Religious truth” conveys nothing clear to me at all.
From 'Scientific Truth' in Essays in Science (1934, 2004), 11.
It is inconceivable, that inanimate brute matter should, without the mediation of something else, which is not material, operate upon and affect other matter without mutual contact … That gravity should be innate, inherent, and essential to matter, so that one body may act upon another at a distance, through a vacuum, without the mediation of anything else, by and through which their action and force may be conveyed from one to another, is to me so great an absurdity, that I believe no man who has in philosophical matters a competent faculty of thinking, can ever fall into it. Gravity must be caused by an agent, acting constantly according to certain laws; but whether this agent be material or immaterial, I have left to the consideration of my readers.
Third letter to Bentley, 25 Feb 1693. Quoted in The Works of Richard Bentley, D.D. (1838), Vol. 3, 212-3.
It is now necessary to indicate more definitely the reason why mathematics not only carries conviction in itself, but also transmits conviction to the objects to which it is applied. The reason is found, first of all, in the perfect precision with which the elementary mathematical concepts are determined; in this respect each science must look to its own salvation .... But this is not all. As soon as human thought attempts long chains of conclusions, or difficult matters generally, there arises not only the danger of error but also the suspicion of error, because since all details cannot be surveyed with clearness at the same instant one must in the end be satisfied with a belief that nothing has been overlooked from the beginning. Every one knows how much this is the case even in arithmetic, the most elementary use of mathematics. No one would imagine that the higher parts of mathematics fare better in this respect; on the contrary, in more complicated conclusions the uncertainty and suspicion of hidden errors increases in rapid progression. How does mathematics manage to rid itself of this inconvenience which attaches to it in the highest degree? By making proofs more rigorous? By giving new rules according to which the old rules shall be applied? Not in the least. A very great uncertainty continues to attach to the result of each single computation. But there are checks. In the realm of mathematics each point may be reached by a hundred different ways; and if each of a hundred ways leads to the same point, one may be sure that the right point has been reached. A calculation without a check is as good as none. Just so it is with every isolated proof in any speculative science whatever; the proof may be ever so ingenious, and ever so perfectly true and correct, it will still fail to convince permanently. He will therefore be much deceived, who, in metaphysics, or in psychology which depends on metaphysics, hopes to see his greatest care in the precise determination of the concepts and in the logical conclusions rewarded by conviction, much less by success in transmitting conviction to others. Not only must the conclusions support each other, without coercion or suspicion of subreption, but in all matters originating in experience, or judging concerning experience, the results of speculation must be verified by experience, not only superficially, but in countless special cases.
In Werke [Kehrbach] (1890), Bd. 5, 105. As quoted, cited and translated in Robert Édouard Moritz, Memorabilia Mathematica; Or, The Philomath’s Quotation-Book (1914), 19.
It is of interest to inquire what happens when the aviator’s speed… approximates to the velocity of light. Lengths in the direction of flight become smaller and smaller, until for the speed of light they shrink to zero. The aviator and the objects accompanying him shrink to two dimensions. We are saved the difficulty of imagining how the processes of life can go on in two dimensions, because nothing goes on. Time is arrested altogether. This is the description according to the terrestrial observer. The aviator himself detects nothing unusual; he does not perceive that he has stopped moving. He is merely waiting for the next instant to come before making the next movement; and the mere fact that time is arrested means that he does not perceive that the next instant is a long time coming.
In Space, Time and Gravitation: An Outline of the General Relativity Theory (1920, 1921), 26.
It is said that the composing of the Lilavati was occasioned by the following circumstance. Lilavati was the name of the author’s daughter, concerning whom it appeared, from the qualities of the ascendant at her birth, that she was destined to pass her life unmarried, and to remain without children. The father ascertained a lucky hour for contracting her in marriage, that she might be firmly connected and have children. It is said that when that hour approached, he brought his daughter and his intended son near him. He left the hour cup on the vessel of water and kept in attendance a time-knowing astrologer, in order that when the cup should subside in the water, those two precious jewels should be united. But, as the intended arrangement was not according to destiny, it happened that the girl, from a curiosity natural to children, looked into the cup, to observe the water coming in at the hole, when by chance a pearl separated from her bridal dress, fell into the cup, and, rolling down to the hole, stopped the influx of water. So the astrologer waited in expectation of the promised hour. When the operation of the cup had thus been delayed beyond all moderate time, the father was in consternation, and examining, he found that a small pearl had stopped the course of the water, and that the long-expected hour was passed. In short, the father, thus disappointed, said to his unfortunate daughter, I will write a book of your name, which shall remain to the latest times—for a good name is a second life, and the ground-work of eternal existence.
In Preface to the Persian translation of the Lilavati by Faizi (1587), itself translated into English by Strachey and quoted in John Taylor (trans.) Lilawati, or, A Treatise on Arithmetic and Geometry by Bhascara Acharya (1816), Introduction, 3. [The Lilavati is the 12th century treatise on mathematics by Indian mathematician, Bhaskara Acharya, born 1114.]
It is the duty of every citizen according to his best capacities to give validity to his convictions in political affairs.
…...
It is to geometry that we owe in some sort the source of this discovery [of beryllium]; it is that [science] that furnished the first idea of it, and we may say that without it the knowledge of this new earth would not have been acquired for a long time, since according to the analysis of the emerald by M. Klaproth and that of the beryl by M. Bindheim one would not have thought it possible to recommence this work without the strong analogies or even almost perfect identity that Citizen Haüy found for the geometrical properties between these two stony fossils.
Haüy used the geometry of cleavage to reveal the underlying crystal structure, and thus found the emeral and beryl were geometrically identical. In May Elvira Weeks, The Discovery of the Elements (1934), 153, citing Mellor, Comprehensive Treatise on Inorganic and Theoretical Chemistry (1923), 204-7.
It was Plato, according to Sosigenes, who set this as a problem for those concerned with these things, through what suppositions of uniform and ordered movements the appearances concerning the movements of the wandering heavenly bodies could be preserved.
— Plato
Simplicius, On Aristotle's On the Heavens, 488.21. Trans. R. W. Sharples.
It would appear that Deductive and Demonstrative Sciences are all, without exception, Inductive Sciences: that their evidence is that of experience, but that they are also, in virtue of the peculiar character of one indispensable portion of the general formulae according to which their inductions are made, Hypothetical Sciences. Their conclusions are true only upon certain suppositions, which are, or ought to be, approximations to the truth, but are seldom, if ever, exactly true; and to this hypothetical character is to be ascribed the peculiar certainty, which is supposed to be inherent in demonstration.
In System of Logic, Bk. 2, chap. 6, 1.
John Bardeen was an avid golfer and a good one. Whenever possible, he sought out golf courses during research or consulting trips. According to the stories, he was as proud of hitting a “hole in one” as he was to win a second Nobel Prize.
In 'John Bardeen: A Place to Win Two Nobel Prizes and Make a Hole in One', collected in Lillian Hoddeson (ed.), No Boundaries: University of Illinois Vignettes (2004), Chap. 16, 257.
Let me describe briefly how a black hole might be created. Imagine a star with a mass 10 times that of the sun. During most of its lifetime of about a billion years the star will generate heat at its center by converting hydrogen into helium. The energy released will create sufficient pressure to support the star against its own gravity, giving rise to an object with a radius about five times the radius of the sun. The escape velocity from the surface of such a star would be about 1,000 kilometers per second. That is to say, an object fired vertically upward from the surface of the star with a velocity of less than 1,000 kilometers per second would be dragged back by the gravitational field of the star and would return to the surface, whereas an object with a velocity greater than that would escape to infinity.
When the star had exhausted its nuclear fuel, there would be nothing to maintain the outward pressure, and the star would begin to collapse because of its own gravity. As the star shrank, the gravitational field at the surface would become stronger and the escape velocity would increase. By the time the radius had got down to 10 kilometers the escape velocity would have increased to 100,000 kilometers per second, the velocity of light. After that time any light emitted from the star would not be able to escape to infinity but would be dragged back by the gravitational field. According to the special theory of relativity nothing can travel faster than light, so that if light cannot escape, nothing else can either. The result would be a black hole: a region of space-time from which it is not possible to escape to infinity.
When the star had exhausted its nuclear fuel, there would be nothing to maintain the outward pressure, and the star would begin to collapse because of its own gravity. As the star shrank, the gravitational field at the surface would become stronger and the escape velocity would increase. By the time the radius had got down to 10 kilometers the escape velocity would have increased to 100,000 kilometers per second, the velocity of light. After that time any light emitted from the star would not be able to escape to infinity but would be dragged back by the gravitational field. According to the special theory of relativity nothing can travel faster than light, so that if light cannot escape, nothing else can either. The result would be a black hole: a region of space-time from which it is not possible to escape to infinity.
'The Quantum Mechanics of Black Holes', Scientific American, 1977, 236, 34-40.
Let us now declare the means whereby our understanding can rise to knowledge without fear of error. There are two such means: intuition and deduction. By intuition I mean not the varying testimony of the senses, nor the deductive judgment of imagination naturally extravagant, but the conception of an attentive mind so distinct and so clear that no doubt remains to it with regard to that which it comprehends; or, what amounts to the same thing, the self-evidencing conception of a sound and attentive mind, a conception which springs from the light of reason alone, and is more certain, because more simple, than deduction itself. …
It may perhaps be asked why to intuition we add this other mode of knowing, by deduction, that is to say, the process which, from something of which we have certain knowledge, draws consequences which necessarily follow therefrom. But we are obliged to admit this second step; for there are a great many things which, without being evident of themselves, nevertheless bear the marks of certainty if only they are deduced from true and incontestable principles by a continuous and uninterrupted movement of thought, with distinct intuition of each thing; just as we know that the last link of a long chain holds to the first, although we can not take in with one glance of the eye the intermediate links, provided that, after having run over them in succession, we can recall them all, each as being joined to its fellows, from the first up to the last. Thus we distinguish intuition from deduction, inasmuch as in the latter case there is conceived a certain progress or succession, while it is not so in the former; … whence it follows that primary propositions, derived immediately from principles, may be said to be known, according to the way we view them, now by intuition, now by deduction; although the principles themselves can be known only by intuition, the remote consequences only by deduction.
It may perhaps be asked why to intuition we add this other mode of knowing, by deduction, that is to say, the process which, from something of which we have certain knowledge, draws consequences which necessarily follow therefrom. But we are obliged to admit this second step; for there are a great many things which, without being evident of themselves, nevertheless bear the marks of certainty if only they are deduced from true and incontestable principles by a continuous and uninterrupted movement of thought, with distinct intuition of each thing; just as we know that the last link of a long chain holds to the first, although we can not take in with one glance of the eye the intermediate links, provided that, after having run over them in succession, we can recall them all, each as being joined to its fellows, from the first up to the last. Thus we distinguish intuition from deduction, inasmuch as in the latter case there is conceived a certain progress or succession, while it is not so in the former; … whence it follows that primary propositions, derived immediately from principles, may be said to be known, according to the way we view them, now by intuition, now by deduction; although the principles themselves can be known only by intuition, the remote consequences only by deduction.
In Rules for the Direction of the Mind, Philosophy of Descartes. [Torrey] (1892), 64-65.
Let us now discuss the extent of the mathematical quality in Nature. According to the mechanistic scheme of physics or to its relativistic modification, one needs for the complete description of the universe not merely a complete system of equations of motion, but also a complete set of initial conditions, and it is only to the former of these that mathematical theories apply. The latter are considered to be not amenable to theoretical treatment and to be determinable only from observation.
From Lecture delivered on presentation of the James Scott prize, (6 Feb 1939), 'The Relation Between Mathematics And Physics', printed in Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (1938-1939), 59, Part 2, 125.
Linnaeus had it constantly in mind:“The closer we get to know the creatures around us, the clearer is the understanding we obtain of the chain of nature, and its harmony and system, according to which all things appear to have been created.”
In 'The Two Faces of Linnaeus', in Tore Frängsmyr (ed.), Linnaeus: The Man and his Work (1983, 1994), 16. Quoted in David Weinberger, Everything is Miscellaneous (2007), 241.
Man cannot have an effect on nature, cannot adopt any of her forces, if he does not know the natural laws in terms of measurement and numerical relations. Here also lies the strength of the national intelligence, which increases and decreases according to such knowledge. Knowledge and comprehension are the joy and justification of humanity; they are parts of the national wealth, often a replacement for the materials that nature has too sparcely dispensed. Those very people who are behind us in general industrial activity, in application and technical chemistry, in careful selection and processing of natural materials, such that regard for such enterprise does not permeate all classes, will inevitably decline in prosperity; all the more so were neighbouring states, in which science and the industrial arts have an active interrelationship, progress with youthful vigour.
Kosmos (1845), vol.1, 35. Quoted in C. C. Gillispie (ed.), Dictionary of Scientific Biography (1970), vol. 6, 552.
Man is only a moral being because he lives in society, since morality consists in solidarity with the group, and varies according to that solidarity. Cause all social life to vanish, and moral life would vanish at the same time, having no object to cling to.
The Division of Labour in Society (1893), trans. W. D. Halls (1984), 331.
Mathematics is a game played according to certain simple rules with meaningless marks on paper.
Given as narrative, without quotation marks, in Eric Temple Bell, Mathematics, Queen and Servant of Science (1951, 1961), 21.
Mathematics is not only one of the most valuable inventions—or discoveries—of the human mind, but can have an aesthetic appeal equal to that of anything in art. Perhaps even more so, according to the poetess who proclaimed, “Euclid alone hath looked at beauty bare.”
From 'The Joy of Maths'. Collected in Arthur C. Clarke, Greetings, Carbon-Based Bipeds!: Collected Essays, 1934-1998, 460.
Mathematics, from the earliest times to which the history of human reason can reach, has followed, among that wonderful people of the Greeks, the safe way of science. But it must not be supposed that it was as easy for mathematics as for logic, in which reason is concerned with itself alone, to find, or rather to make for itself that royal road. I believe, on the contrary, that there was a long period of tentative work (chiefly still among the Egyptians), and that the change is to be ascribed to a revolution, produced by the happy thought of a single man, whose experiments pointed unmistakably to the path that had to be followed, and opened and traced out for the most distant times the safe way of a science. The history of that intellectual revolution, which was far more important than the passage round the celebrated Cape of Good Hope, and the name of its fortunate author, have not been preserved to us. … A new light flashed on the first man who demonstrated the properties of the isosceles triangle (whether his name was Thales or any other name), for he found that he had not to investigate what he saw in the figure, or the mere concepts of that figure, and thus to learn its properties; but that he had to produce (by construction) what he had himself, according to concepts a priori, placed into that figure and represented in it, so that, in order to know anything with certainty a priori, he must not attribute to that figure anything beyond what necessarily follows from what he has himself placed into it, in accordance with the concept.
In Critique of Pure Reason, Preface to the Second Edition, (1900), 690.
Most loss of life and property has been due to the collapse of antiquated and unsafe structures, mostly of brick and other masonry. ... There is progress of California toward building new construction according to earthquake-resistant design. We would have less reason to ask for earthquake prediction if this was universal.
From interview with Henry Spall, as in an abridged version of Earthquake Information Bulletin (Jan-Feb 1980), 12, No. 1, that was on the USGS website.
Nature becomes fertile only by virtue of laws that oblige matter to organize itself into one of a number of necessarily very simple primitive forms. Because of their very simplicity, these are capable of constituting the basis for increasingly complex bodies, by the addition of organs calculated according to identical laws of possibility.
'Matiere', Dictionnaire Classique d' Histoire Naturelle (1822-31), Vol. 10, 277, trans. J. Mandelbaum. Quoted in Pietro Corsi, The Age of Lamarck (1988), 225.
Nature even in chaos cannot proceed otherwise than regularly and according to order.
Universal Natural History and Theory of the Heavens (1755), editted and translated by William Hastie in Kant's Cosmogony (1900), 26.
Nature goes her own way, and all that to us seems an exception is really according to order.
Thurs 9 Dec 1824. Johann Peter Eckermann, Conversations with Goethe, ed. J. K. Moorhead and trans. J. Oxenford (1971), 75.
Nature, everywhere the most amazingly and outstandingly remarkable producer of living bodies, being most carefully arranged according to physical, mechanical, and chemical laws, does not give even the smallest hint of its extraordinary and tireless workings and quite clearly points to its work as being alone worthy of a benign and omnipotent God; and it carries this bright quality in all of its traces, in that, just as all of its general mechanisms rejoice, so also do all of their various smallest component parts rejoice in the depth of wisdom, in the height of perfection, and in the lofty arrangement of forms and qualities, which lie far beyond every investigation of the human mind.
'Inaugural Physico-Medical Dissertation on the Blood and the Circulation of the Microcosm' (1749). Trans. Arthur Donovan and Joseph Prentiss, James Hutton's Medical Dissertation (1980), 29.
Now it is a well-known principle of zoological evolution that an isolated region, if large and sufficiently varied in its topography, soil, climate and vegetation, will give rise to a diversified fauna according to the law of adaptive radiation from primitive and central types. Branches will spring off in all directions to take advantage of every possible opportunity of securing food. The modifications which animals undergo in this adaptive radiation are largely of mechanical nature, they are limited in number and kind by hereditary, stirp or germinal influences, and thus result in the independent evolution of similar types in widely-separated regions under the law of parallelism or homoplasy. This law causes the independent origin not only of similar genera but of similar families and even of our similar orders. Nature thus repeats herself upon a vast scale, but the similarity is never complete and exact.
'The Geological and Faunal Relations of Europe and America during the Tertiary Period and the Theory of the Successive Invasions of an African Fauna', Science (1900), 11, 563-64.
On our planet, all objects are subject to continual and inevitable changes which arise from the essential order of things. These changes take place at a variable rate according to the nature, condition, or situation of the objects involved, but are nevertheless accomplished within a certain period of time. Time is insignificant and never a difficulty for Nature. It is always at her disposal and represents an unlimited power with which she accomplishes her greatest and smallest tasks.
Hydrogéologie (1802), trans. A. V. Carozzi (1964), 61.
One of the most immediate consequences of the electrochemical theory is the necessity of regarding all chemical compounds as binary substances. It is necessary to discover in each of them the positive and negative constituents... No view was ever more fitted to retard the progress of organic chemistry. Where the theory of substitution and the theory of types assume similar molecules, in which some of the elements can be replaced by others without the edifice becoming modified either in form or outward behaviour, the electrochemical theory divides these same molecules, simply and solely, it may be said, in order to find in them two opposite groups, which it then supposes to be combined with each other in virtue of their mutual electrical activity... I have tried to show that in organic chemistry there exist types which are capable, without destruction, of undergoing the most singular transformations according to the nature of the elements.
Traité de Chemie Appliquée aux Arts, Vol. I (1828), 53. Trans. J. R. Partington, A History of Chemistry, Vol. 4, 366.
One should not wrongly reify “cause” and “effect,” as the natural scientists do (and whoever, like them, now “naturalizes” in his thinking), according to the prevailing mechanical doltishness which makes the cause press and push until it “effects” its end; one should use “cause” and “effect” only as pure concepts, that is to say, as conventional fictions for the purpose of designation and communication—not for explanation.
In Beyond Good and Evil (1886). Trans. W. Kaufmann (ed.), Basic Writings of Nietzsche (1968), 219.
Our system of philosophy is itself on trial; it must stand or fall according as it is broad enough to find room for this experience as an element of life.
Swarthmore Lecture (1929) at Friends’ House, London, printed in Science and the Unseen World (1929), 46.
Parasites are not only incredibly diverse; they are also incredibly successful. There are parasitic stretches of DNA in your own genes, some of which are called retrotransposons. Many of the parasitic stretches were originally viruses that entered our DNA. Most of them don't do us any harm. They just copy and insert themselves in other parts of our DNA, basically replicating themselves. Sometimes they hop into other species and replicate themselves in a new host. According to one estimate, roughly one-third to one-half of all human DNA is basically parasitic.
Talk at Columbia University, 'The Power of Parasites.'
People are entirely too disbelieving of coincidence. They are far too ready to dismiss it and to build arcane structures of extremely rickety substance in order to avoid it. I, on the other hand, see coincidence everywhere as an inevitable consequence of the laws of probability, according to which having no unusual coincidence is far more unusual than any coincidence could possibly be.
In The Planet That Wasn't (1976), 3.
Physicians are some of them so pleasing and conformable to the humour of the patient, as they press not the true cure of the disease : and some other are so regular in proceeding according to art for the disease, as they respect not sufficiently the condition of the patient.
XXX. Of Regimen of Health,' Essays (1597). In Francis Bacon and Basil Montagu, The Works of Francis Bacon, Lord Chancellor of England (1852), 39.
Positivism is a theory of knowledge according to which the only kind of sound knowledge available to human kind is that if science grounded in observation.
(1891). As given as an epigraph in M.J. Vinod and Meena Deshpande, Contemporary Political Theory (2013), 3.
Primates stand at a turning point in the course of evolution. Primates are to the biologist what viruses are to the biochemist. They can be analysed and partly understood according to the rules of a simpler discipline, but they also present another level of complexity: viruses are living chemicals, and primates are animals who love and hate and think.
'The Evolution of Primate Behavior: A survey of the primate order traces the progressive development of intelligence as a way of life', American Scientist (1985), 73, 288.
Quantity is that which is operated with according to fixed mutually consistent laws. Both operator and operand must derive their meaning from the laws of operation. In the case of ordinary algebra these are the three laws already indicated [the commutative, associative, and distributive laws], in the algebra of quaternions the same save the law of commutation for multiplication and division, and so on. It may be questioned whether this definition is sufficient, and it may be objected that it is vague; but the reader will do well to reflect that any definition must include the linear algebras of Peirce, the algebra of logic, and others that may be easily imagined, although they have not yet been developed. This general definition of quantity enables us to see how operators may be treated as quantities, and thus to understand the rationale of the so called symbolical methods.
In 'Mathematics', Encyclopedia Britannica (9th ed.).
Racism is an ism to which everyone in the world today is exposed; for or against, we must take sides. And the history of the future will differ according to the decision which we make.
In Race: Science and Politics (1945), 5.
Science has hitherto been proceeding without the guidance of any rational theory of logic, and has certainly made good progress. It is like a computer who is pursuing some method of arithmetical approximation. Even if he occasionally makes mistakes in his ciphering, yet if the process is a good one they will rectify themselves. But then he would approximate much more rapidly if he did not commit these errors; and in my opinion, the time has come when science ought to be provided with a logic. My theory satisfies me; I can see no flaw in it. According to that theory universality, necessity, exactitude, in the absolute sense of these words, are unattainable by us, and do not exist in nature. There is an ideal law to which nature approximates; but to express it would require an endless series of modifications, like the decimals expressing surd. Only when you have asked a question in so crude a shape that continuity is not involved, is a perfectly true answer attainable.
Letter to G. F. Becker, 11 June 1893. Merrill Collection, Library of Congress. Quoted in Nathan Reingold, Science in Nineteenth-Century America: A Documentary History (1966), 231-2.
Science is knowledge arranged and classified according to truth, facts, and the general laws of nature.
Interview in San Francisco Bulletin (22 Jan 1926). As cited in Michael C. and Linda Rose Thomsett, A Speaker's Treasury of Quotations: Maxims, Witticisms and Quips for Speeches and Presentations (2009), 102-103. Also in 'Science and Civilization', Prescott Evening Courier (3 Nov 1925), 6.
Science recognizes no personal powers in the universe responsive to the prayers and needs of men. Belief in mysterious powers which constitutes, according to our definition, the conceptual aspect of religion is usually an animistic belief in personal powers. Science in effect denies the existence of spiritual beings which religion affirms.
Religion in Human Affairs (1929), 470.
Scientific wealth tends to accumulate according to the law of compound interest. Every addition to knowledge of the properties of matter supplies the physical scientist with new instrumental means for discovering and interpreting phenomena of nature, which in their turn afford foundations of fresh generalisations, bringing gains of permanent value into the great storehouse of natural philosophy.
From Inaugural Address of the President to British Association for the Advancement of Science, Edinburgh (2 Aug 1871). Printed in The Chemical News (4 Aug 1871), 24, No. 610., 53.
Signs and symptoms indicate the present, past and future states of the three states of the body (health, illness, neutrality). According to Galen, knowledge of the present state is of advantage only to the patient as it helps him to follow the proper course of management. Knowledge of the past state is useful only to the physician inasmuch as its disclosure by him to the patient brings him a greater respect for his professional advice. Knowledge of the future state is useful to both. It gives an opportunity to the patient to be forewarned to adopt necessary preventative measures and it enhances the reputation of the physician by correctly forecasting the future developments.
— Avicenna
'The Signs and Symptoms (Diagnosis): General Remarks,' in The Canon of Medicine, adapted by L. Bakhtiar (1999), 259.
So God created the great sea monsters and every living creature that moves, with which the waters swarm, according to their kinds.
— Bible
(circa 725 B.C.)
Somewhere between 1900 and 1912 in this country, according to one sober medical scientist [Henderson] a random patient, with a random disease, consulting a doctor chosen at random had, for the first time in the history of mankind, a better than fifty-fifty chance of profiting from the encounter.
Quoted in New England Journal of Medicine (1964), 270, 449.
Suppose that you are in love with a lady on Neptune and that she returns the sentiment. It will be some consolation for the melancholy separation if you can say to yourself at some possibly pre-arranged moment, “She is thinking of me now.” Unfortunately a difficulty has arisen because we have had to abolish Now. There is no absolute Now, but only the various relative Nows, differing according to their reckoning of different observers and covering the whole neutral wedge which at the distance of Neptune is about eight hours thick. She will have to think of you continuously for eight hours on end in order to circumvent the ambiguity “Now.”
In The Nature of the Physical World (1929), 49.
Tait dubbed Maxwell dp/dt, for according to thermodynamics dp/dt = JCM (where C denotes Carnot’s function) the initials of (J.C.) Maxwell’s name. On the other hand Maxwell denoted Thomson by T and Tait by T'; so that it became customary to quote Thomson and Tait’s Treatise on Natural Philosophy as T and T'.
In Bibliotheca Mathematica (1903), 3, 187. As cited in Robert Édouard Moritz, Memorabilia Mathematica; Or, The Philomath’s Quotation-Book (1914), 178. [Note: Thomson is William Thomson, later Lord Kelvin. —Webmaster.]
That special substance according to whose mass and degree of development all the creatures of this world take rank in the scale of creation, is not bone, but brain.
The Foot-prints of the Creator: Or, The Asterolepis of Stromness (1850, 1859), 160.
The 4th sort of creatures... which moved through the 3 former sorts, were incredibly small, and so small in my eye that I judged, that if 100 of them lay [stretched out] one by another, they would not equal the length of a grain of course Sand; and according to this estimate, ten hundred thousand of them could not equal the dimensions of a grain of such course Sand. There was discover’d by me a fifth sort, which had near the thickness of the former, but they were almost twice as long.
The first time bacteria were observed.
The first time bacteria were observed.
Letter to H. Oldenburg, 9 Oct 1676. In The Collected Letters of Antoni van Leeuwenhoek (1957), Vol. 2, 95.
The axioms of geometry are—according to my way of thinking—not arbitrary, but sensible. statements, which are, in general, induced by space perception and are determined as to their precise content by expediency.
In George Edward Martin, The Foundations of Geometry and the Non-Euclidean Plane (1982), 142.
The cause of rain is now, I consider, no longer an object of doubt. If two masses of air of unequal temperatures, by the ordinary currents of the winds, are intermixed, when saturated with vapour, a precipitation ensues. If the masses are under saturation, then less precipitation takes place, or none at all, according to the degree. Also, the warmer the air, the greater is the quantity of vapour precipitated in like circumstances. ... Hence the reason why rains are heavier in summer than in winter, and in warm countries than in cold.
Memoirs of the Literary and Philosophical Society of Manchester (1819), 3, 507. Quoted in George Drysdale Dempsey and Daniel Kinnear Clark, On the Drainage of Lands, Towns, & Buildings (1887), 246.
The desire for guidance, love, and support prompts men to form the social or moral conception of God. This is the God of Providence, who protects, disposes, rewards, and punishes; the God who, according to the limits of the believer’s outlook, loves and cherishes the life of the tribe or of the human race, or even or life itself; the comforter in sorrow and unsatisfied longing; he who preserves the souls of the dead. This is the social or moral conception of God.
…...
The Epicureans, according to whom animals had no creation, doe suppose that by mutation of one into
another, they were first made; for they are the substantial part of the world; like as Anaxagoras and
Euripides affirme in these tearmes: nothing dieth, but in changing as they doe one for another they show sundry formes.
— Plutarch
Fom Morals, translated by Philemon Holland, The Philosophie, Commonlie Called, the Moral Written by the Learned Philosopher Plutarch of Chæronea (1603), 846. As cited in Harris Hawthorne Wilder, History of the Human Body (1909), 26.
The errors of definitions multiply themselves according as the reckoning proceeds; and lead men into absurdities, which at last they see but cannot avoid, without reckoning anew from the beginning.
In Thomas Hobbes and William Molesworth (ed.) Leviathan: Or the Matter, Form and Power of a Commonwealth Ecclesiastical and Civil (1839), Vol. 3, 24.
The essential fact is simply that all the pictures which science now draws of nature, and which alone seem capable of according with observational facts, are mathematical pictures. … It can hardly be disputed that nature and our conscious mathematical minds work according to the same laws.
In The Mysterious Universe (1930, 1932), 149 & 162.
The focal points of our different reflections have been called “science”’ or “art” according to the nature of their “formal” objects, to use the language of logic. If the object leads to action, we give the name of “art” to the compendium of rules governing its use and to their technical order. If the object is merely contemplated under different aspects, the compendium and technical order of the observations concerning this object are called “science.” Thus metaphysics is a science and ethics is an art. The same is true of theology and pyrotechnics.
Definition of 'Art', Encyclopédie (1751). Translated by Nelly S. Hoyt and Thomas Cassirer (1965), 4.
The function of Art is to imitate Nature in her manner of operation. Our understanding of “her manner of operation” changes according to advances in the sciences.
A Year from Monday (1969), 31.
The great revelation of the quantum theory was that features of discreteness were discovered in the Book of Nature, in a context in which anything other than continuity seemed to be absurd according to the views held until then.
What is Life? (1944), 48.
The History of Evolution of Organisms consists of two kindred and closely connected parts: Ontogeny, which is the history of the evolution of individual organisms, and Phylogeny, which is the history of the evolution of organic tribes. Ontogency is a brief and rapid recapitulation of Phylogeny, dependent on the physiological functions of Heredity (reproduction) and Adaptation (nutrition). The individual organism reproduces in the rapid and short course of its own evolution the most important of the changes in form through which its ancestors, according to laws of Heredity and Adaptation, have passed in the slow and long course of their palaeontological evolution.
Translated from his Generelle Morphologie (1866) as an epigraph to Chap. 1, The Evolution of Man, (1886), Vol 1, 1-2.
The laws of nature are the rules according to which the effects are produced; but there must be a cause which operates according to these rules. The laws of navigation never navigated a ship. The rules of architecture never built a house.
'Essay I: On Active Power In General: Chapter 6: On the Efficient Causes of the Phenomena of Nature', Essays on the Active Powers of Man (1785), Chap. 6, 47.
The lives of scientists, considered as Lives, almost always make dull reading. For one thing, the careers of the famous and the merely ordinary fall into much the same pattern, give or take an honorary degree or two, or (in European countries) an honorific order. It could be hardly otherwise. Academics can only seldom lead lives that are spacious or exciting in a worldly sense. They need laboratories or libraries and the company of other academics. Their work is in no way made deeper or more cogent by privation, distress or worldly buffetings. Their private lives may be unhappy, strangely mixed up or comic, but not in ways that tell us anything special about the nature or direction of their work. Academics lie outside the devastation area of the literary convention according to which the lives of artists and men of letters are intrinsically interesting, a source of cultural insight in themselves. If a scientist were to cut his ear off, no one would take it as evidence of a heightened sensibility; if a historian were to fail (as Ruskin did) to consummate his marriage, we should not suppose that our understanding of historical scholarship had somehow been enriched.
'J.B.S: A Johnsonian Scientist', New York Review of Books (10 Oct 1968), reprinted in Pluto's Republic (1982), and inThe Strange Case of the Spotted Mice and Other Classic Essays on Science (1996), 86.
The living being is stable. It must be so in order not to be destroyed, dissolved, or disintegrated by the colossal forces, often adverse, which surround it. By apparent contradiction it maintains its stability only if it is excitable and capable of modifying itself according to external stimuli and adjusting its response to the stimulation. In a sense it is stable because it is modifiable—the slight instability is the necessary condition for the true stability of the organism.
In Dictionnaire de Physiologie (1900), Vol. 4, 72. English as quoted in Walter Bradford Cannon, The Wisdom of the Body (1932), 21, with French source citation footnoted on 26.
The maintenance of biological diversity requires special measures that extend far beyond the establishment of nature reserves. Several reasons for this stand out. Existing reserves have been selected according to a number of criteria, including the desire to protect nature, scenery, and watersheds, and to promote cultural values and recreational opportunities. The actual requirements of individual species, populations, and communities have seldom been known, nor has the available information always been employed in site selection and planning for nature reserves. The use of lands surrounding nature reserves has typically been inimical to conservation, since it has usually involved heavy use of pesticides, industrial development, and the presence of human settlements in which fire, hunting, and firewood gathering feature as elements of the local economy.
The Fragmented Forest: Island Biogeography Theory and the Preservation of Biotic Diversity (1984), xii.
The members of the department became like the Athenians who, according to the Apostle Paul, “spent their time in nothing else, but either to tell or to hear some new thing.” Anyone who thought he had a bright idea rushed out to try it out on a colleague. Groups of two or more could be seen every day in offices, before blackboards or even in corridors, arguing vehemently about these 'brain storms.' It is doubtful whether any paper ever emerged for publication that had not run the gauntlet of such criticism. The whole department thus became far greater than the sum of its individual members.
Obituary of Gilbert Newton Lewis, Biographical Memoirs of the National Academy of Science (1958), 31, 212.
The metaphysical doctrine of determinism simply asserts that all events in this world are fixed, or unalterable, or predetermined. It does not assert that they are known to anybody, or predictable by scientific means. But it asserts that the future is as little changeable as is the past. Everybody knows what we mean when we say that the past cannot be changed. It is in precisely the same sense that the future cannot be changed, according to metaphysical determinism.
Karl Raimund Popper and William Warren Bartley (ed.), The Open Universe: an Argument for Indeterminism (1991), 8.
The mind of a young man (his gallery I mean) is often furnished different ways. According to the scenes he is placed in, so are his pictures. They disappear, and he gets a new set in a moment. But as he grows up, he gets some substantial pieces which he always preserves, although he may alter his smaller paintings in a moment.
The mortality of those who dig minerals is very great, and women who marry men of this sort marry again and again. According to Agricola, at the mines in the Carpathian mountains, women have been known to marry seven times.
Diseases of Workers, translated by W. C. Wright, preface.
The night before Easter Sunday of that year (1920) I awoke, turned on the light, and jotted down a few notes on a tiny slip of thin paper. Then I fell asleep again. It occurred to me at six o’clock in the morning that during the night I had written down something most important, but I was unable to decipher the scrawl. The next night, at three o’clock, the idea returned. It was the design of an experiment to determine whether the hypothesis of chemical transmission that I had uttered seventeen years ago was correct. I got up immediately, went to the laboratory, and performed a simple experiment on a frog heart according to the nocturnal design. I have to describe this experiment briefly since its results became the foundation of the theory of chemical transmission of the nervous impulse. The hearts of two frogs were isolated, the first with its nerves, the second without. Both hearts were attached to Straub cannulas filled with a little Ringer solution. The vagus nerve of the first heart was stimulated for a few minutes. Then the Ringer solution that had been in the first heart during the stimulation of the vagus was transferred to the second heart. It slowed and its beats diminished just as if its vagus had been stimulated. Similarly, when the accelerator nerve was stimulated and the Ringer from this period transferred, the second heart speeded up and its beats increased. These results unequivocally proved that the nerves do not influence the heart directly but liberate from their terminals specific chemical substances which, in their turn, cause the well-known modifications of the function of the heart characteristic of the stimulation of its nerves.
'An Autobiographic Sketch', Perspectives in Biology and Medicine (1960), 4, 17.
THE OATH. I swear by Apollo [the healing God], the physician and Aesclepius [son of Apollo], and Health [Hygeia], and All-heal [Panacea], and all the gods and goddesses, that, according to my ability and judgment, I will keep this Oath and this stipulation—to reckon him who taught me this Art equally dear to me as my parents, to share my substance with him, and relieve his necessities if required; to look upon his offspring in the same footing as my own brothers, and to teach them this art, if they shall wish to learn it, without fee or stipulation; and that by precept, lecture, and every other mode of instruction, I will impart a knowledge of the Art to my own sons, and those of my teachers, and to disciples bound by a stipulation and oath according to the law of medicine, but to none others. I will follow that system of regimen which, according to my ability and judgment, I consider for the benefit of my patients, and abstain from whatever is deleterious and mischievous. I will give no deadly medicine to any one if asked, nor suggest any such counsel; and in like manner I will not give to a woman a pessary to produce abortion. With purity and with holiness I will pass my life and practice my Art. I will not cut persons laboring under the stone, but will leave this to be done by men who are practitioners of this work. Into whatever houses I enter, I will go into them for the benefit of the sick, and will abstain from every voluntary act of mischief and corruption; and, further, from the seduction of females or males, of freemen and slaves. Whatever, in connection with my professional practice or not, in connection with it, I see or hear, in the life of men, which ought not to be spoken of abroad, I will not divulge, as reckoning that all such should be kept secret. While I continue to keep this Oath unviolated, may it be granted to me to enjoy life and the practice of the art, respected by all men, in all times! But should I trespass and violate this Oath, may the reverse be my lot!
The Genuine Works of Hippocrates, trans. Francis Adams (1886), Vol. 2, 344-5.
The precise equivalence of the chromosomes contributed by the two sexes is a physical correlative of the fact that the two sexes play, on the whole, equal parts in hereditary transmission, and it seems to show that the chromosomal substance, the chromatin, is to be regarded as the physical basis of inheritance. Now, chromatin is known to be closely similar to, if not identical with, a substance known as nuclein (C29H49N9O22, according to Miescher), which analysis shows to be a tolerably definite chemical compased of nucleic acid (a complex organic acid rich in phosphorus) and albumin. And thus we reach the remarkable conclusion that inheritance may, perhaps, be effected by the physical transmission of a particular chemical compound from parent to offspring.
In An Atlas of the Fertilization and Karyokinesis of the Ovum (1895), 4.
The reason it is so hard to attain to something good in any of the arts and sciences is that it involves attaining to a certain stipulated point; to do something badly according to a predetermined rule would be just as hard, if indeed it would then still deserve to be called bad.
Aphorism 53 in Notebook C (1772-1773), as translated by R.J. Hollingdale in Aphorisms (1990). Reprinted as The Waste Books (2000), 42.
The subsequent course of nature, teaches, that God, indeed, gave motion to matter; but that, in the beginning, he so guided the various motion of the parts of it, as to contrive them into the world he design'd they should compose; and establish'd those rules of motion, and that order amongst things corporeal, which we call the laws of nature. Thus, the universe being once fram'd by God, and the laws of motion settled, and all upheld by his perpetual concourse, and general providence; the same philosophy teaches, that the phenomena of the world, are physically produced by the mechanical properties of the parts of matter; and, that they operate upon one another according to mechanical laws. 'Tis of this kind of corpuscular philosophy, that I speak.
'The Excellence and Grounds of the Mechanical Philosophy', In P. Shaw (ed.), The Philosophical Works of Robert Boyle (1725), Vol. 1, 187.
The technologies which have had the most profound effects on human life are usually simple. A good example of a simple technology with profound historical consequences is hay. Nobody knows who invented hay, the idea of cutting grass in the autumn and storing it in large enough quantities to keep horses and cows alive through the winter. All we know is that the technology of hay was unknown to the Roman Empire but was known to every village of medieval Europe. Like many other crucially important technologies, hay emerged anonymously during the so-called Dark Ages. According to the Hay Theory of History, the invention of hay was the decisive event which moved the center of gravity of urban civilization from the Mediterranean basin to Northern and Western Europe. The Roman Empire did not need hay because in a Mediterranean climate the grass grows well enough in winter for animals to graze. North of the Alps, great cities dependent on horses and oxen for motive power could not exist without hay. So it was hay that allowed populations to grow and civilizations to flourish among the forests of Northern Europe. Hay moved the greatness of Rome to Paris and London, and later to Berlin and Moscow and New York. ... Great inventions like hay and printing, whatever their immediate social costs may be, result in a permanent expansion of our horizons, a lasting acquisition of new territory for human bodies and minds to cultivate.
Infinite In All Directions (1988, 2004), 135. The book is a revised version of a series of the Gifford Lectures under the title 'In Praise of Diversity', given at Aberdeen, Scotland.
The technologists claim that if everything works [in a nuclear fission reactor] according to their blueprints, fission energy will be a safe and very attractive solution to the energy needs of the world. ... The real issue is whether their blueprints will work in the real world and not only in a “technological paradise.”...
Opponents of fission energy point out a number of differences between the real world and the “technological paradise.” ... No acts of God can be permitted.
Opponents of fission energy point out a number of differences between the real world and the “technological paradise.” ... No acts of God can be permitted.
'Energy and Environment', Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists (May 1972), 6.
The very closest stars would require many years to visit, even traveling at the speed of light, which is impossible according to Einstein's theory of relativity. Today's fastest spaceships would require 200,000 years to travel to Alpha Centauri, our closest bright star. The energy required to send a hundred colonists to another star, as Frank Drake has pointed out, would be enough to meet the energy needs of the entire United States over a human lifetime. And these estimates are regarding nearby stars. When we consider the distances across the entire galaxy, and between galaxies, interstellar travel seems absolutely untenable.
As co-author with his son, Marshall Fisher, in Strangers in the Night: a Brief History of Life on Other Worlds (1998).
The visible universe is subject to quantification, and is so by necessity. … Between you and me only reason will be the judge … since you proceed according to the rational method, so shall I. … I will also give reason and take it. … This generation has an innate vice. It can’t accept anything that has been discovered by a contemporary!
As quoted in James Burke, The Day the Universe Changed (1985), 41. Burke also quotes the first sentence in The Axemaker's Gift (1995), 112, but after the first ellipsis, is substituted “If you wish to hear more from me, give and take reason, because I am not the kind of man to satisfy his hunger on the picture of a steak!”
The weight of any heavy body of known weight at a particular distance from the center of the world varies according to the variation of its distance therefrom: so that as often as it is removed from the center, it becomes heavier, and when brought near to it, is lighter. On this account, the relation of gravity to gravity is as the relation of distance to distance from the center.
From Book of the Balance of Wisdom. As cited in an epigraph in Charles W. Misner, Kip S. Thorne and John Archibald Wheeler, Gravity (1973), 37.
The work of the inventor consists of conceptualizing, combining, and ordering what is possible according to the laws of nature. This inner working out which precedes the external has a twofold characteristic: the participation of the subconscious in the inventing subject; and that encounter with an external power which demands and obtains complete subjugation, so that the way to the solution is experienced as the fitting of one's own imagination to this power.
Philosophie der Technik (1927). 'Technology in Its Proper Sphere' translated by William Carroll. In Carl Mitcham (ed.) and Robert Mackey (ed.), Philosophy and Technology: Readings in the Philosophical Problems of Technology, (1972), Vol. 14, 321. In David Lovekin, Technique, Discourse, and Consciousness (1991), 73.
The world is comparable to ice, and the Truth to water, the origin of this ice. The name “ice” is only lent to this coagulation; it is the name of water which is restored to it, according to its essential reality.
— Al- Jill
Universal Man. In Seyyed Hossein Nasr, Science and Civilisation in Islam (1968), 341.
The world’s first spaceship, Vostok (East), with a man on board was launched into orbit from the Soviet Union on April 12, 1961. The pilot space-navigator of the satellite-spaceship Vostok is a citizen of the U.S.S.R., Flight Major Yuri Gagarin.
The launching of the multistage space rocket was successful and, after attaining the first escape velocity and the separation of the last stage of the carrier rocket, the spaceship went in to free flight on around-the-earth orbit. According to preliminary data, the period of revolution of the satellite spaceship around the earth is 89.1 min. The minimum distance from the earth at perigee is 175 km (108.7 miles) and the maximum at apogee is 302 km (187.6 miles), and the angle of inclination of the orbit plane to the equator is 65º 4’. The spaceship with the navigator weighs 4725 kg (10,418.6 lb), excluding the weight of the final stage of the carrier rocket.
The first man in space was announced by the Soviet newsagency Tass on 12 April 1961, 9:59 a.m. Moscow time.
The launching of the multistage space rocket was successful and, after attaining the first escape velocity and the separation of the last stage of the carrier rocket, the spaceship went in to free flight on around-the-earth orbit. According to preliminary data, the period of revolution of the satellite spaceship around the earth is 89.1 min. The minimum distance from the earth at perigee is 175 km (108.7 miles) and the maximum at apogee is 302 km (187.6 miles), and the angle of inclination of the orbit plane to the equator is 65º 4’. The spaceship with the navigator weighs 4725 kg (10,418.6 lb), excluding the weight of the final stage of the carrier rocket.
The first man in space was announced by the Soviet newsagency Tass on 12 April 1961, 9:59 a.m. Moscow time.
— Tass
Quoted in John David Anderson, Jr., Hypersonic and High Temperature Gas Dynamics (2000), 2.
There are four classes of Idols which beset men’s minds. To these for distinction’s sake I have assigned names,—calling the first class Idols of the Tribe; the second, Idols of the Cave; the third, Idols of the Market Place; the fourth, Idols of the Theatre …
The Idols of the Tribe have their foundation in human nature itself, and in the tribe or race of men. For it is a false assertion that the sense of man is the measure of things. On the contrary, all perceptions as well of the sense as of the mind are according to the measure of the individual and not according to the measure of the universe. And the human understanding is like a false mirror, which, receiving rays irregularly, distorts and discolours the nature of things by mingling its own nature with it.
The Idols of the Cave are the idols of the individual man. For every one (besides the errors common to human nature in general) has a cave or den of his own, which refracts and discolours the light of nature; owing either to his own proper and peculiar nature; or to his education and conversation with others; or to the reading of books, and the authority of those whom he esteems and admires; or to the differences of impressions, accordingly as they take place in a mind preoccupied and predisposed or in a mind indifferent and settled; or the like.
There are also Idols formed by the intercourse and association of men with each other, which I call Idols of the Market-place, on account of the commerce and consort of men there. For it is by discourse that men associate; and words are imposed according to the apprehension of the vulgar, and therefore the ill and unfit choice of words wonderfully obstructs the understanding. Nor do the definitions or explanations where with in some things learned men are wont to guard and defend themselves, by any means set the matter right. But words plainly force and overrule the understanding, and throw all into confusion, and lead men away into numberless empty controversies and idle fancies.
Lastly, there are Idols which have immigrated into men’s minds from the various dogmas of philosophies, and also from wrong laws of demonstration. These I call Idols of the Theatre; because in my judgment all the received systems are but so many stage-plays, representing worlds of their own creation after an unreal and scenic fashion.
The Idols of the Tribe have their foundation in human nature itself, and in the tribe or race of men. For it is a false assertion that the sense of man is the measure of things. On the contrary, all perceptions as well of the sense as of the mind are according to the measure of the individual and not according to the measure of the universe. And the human understanding is like a false mirror, which, receiving rays irregularly, distorts and discolours the nature of things by mingling its own nature with it.
The Idols of the Cave are the idols of the individual man. For every one (besides the errors common to human nature in general) has a cave or den of his own, which refracts and discolours the light of nature; owing either to his own proper and peculiar nature; or to his education and conversation with others; or to the reading of books, and the authority of those whom he esteems and admires; or to the differences of impressions, accordingly as they take place in a mind preoccupied and predisposed or in a mind indifferent and settled; or the like.
There are also Idols formed by the intercourse and association of men with each other, which I call Idols of the Market-place, on account of the commerce and consort of men there. For it is by discourse that men associate; and words are imposed according to the apprehension of the vulgar, and therefore the ill and unfit choice of words wonderfully obstructs the understanding. Nor do the definitions or explanations where with in some things learned men are wont to guard and defend themselves, by any means set the matter right. But words plainly force and overrule the understanding, and throw all into confusion, and lead men away into numberless empty controversies and idle fancies.
Lastly, there are Idols which have immigrated into men’s minds from the various dogmas of philosophies, and also from wrong laws of demonstration. These I call Idols of the Theatre; because in my judgment all the received systems are but so many stage-plays, representing worlds of their own creation after an unreal and scenic fashion.
From Novum Organum (1620), Book 1, Aphorisms 39, 41-44. Translated as The New Organon: Aphorisms Concerning the Interpretation of Nature and the Kingdom of Man), collected in James Spedding, Robert Ellis and Douglas Heath (eds.), The Works of Francis Bacon (1857), Vol. 4, 53-55.
There are many arts and sciences of which a miner should not be ignorant. First there is Philosophy, that he may discern the origin, cause, and nature of subterranean things; for then he will be able to dig out the veins easily and advantageously, and to obtain more abundant results from his mining. Secondly there is Medicine, that he may be able to look after his diggers and other workman ... Thirdly follows astronomy, that he may know the divisions of the heavens and from them judge the directions of the veins. Fourthly, there is the science of Surveying that he may be able to estimate how deep a shaft should be sunk … Fifthly, his knowledge of Arithmetical Science should be such that he may calculate the cost to be incurred in the machinery and the working of the mine. Sixthly, his learning must comprise Architecture, that he himself may construct the various machines and timber work required underground … Next, he must have knowledge of Drawing, that he can draw plans of his machinery. Lastly, there is the Law, especially that dealing with metals, that he may claim his own rights, that he may undertake the duty of giving others his opinion on legal matters, that he may not take another man’s property and so make trouble for himself, and that he may fulfil his obligations to others according to the law.
In De Re Metallica (1556), trans. H.C. and L.H. Hoover (1950), 3-4.
There has never been just 'coach class' health care, but with these amenities you are seeing people get priorities according to your ability to pay. It's one thing to say you get perks; it's another to say you can buy your way to the head of the line.
Quoted in Nancy S. Tilghman, 'Southampton Hospital Drops V.I.P. Idea', New York Times (27 Jun 2004), L13.
There is an influence which is getting strong and stronger day by day, which shows itself more and more in all departments of human activity, and influence most fruitful and beneficial—the influence of the artist. It was a happy day for the mass of humanity when the artist felt the desire of becoming a physician, an electrician, an engineer or mechanician or—whatnot—a mathematician or a financier; for it was he who wrought all these wonders and grandeur we are witnessing. It was he who abolished that small, pedantic, narrow-grooved school teaching which made of an aspiring student a galley-slave, and he who allowed freedom in the choice of subject of study according to one's pleasure and inclination, and so facilitated development.
'Roentgen Rays or Streams', Electrical Review (12 Aug 1896). Reprinted in The Nikola Tesla Treasury (2007), 307.
By Nikola Tesla
There is in Nature a general prototype in each species on which each individual is modeled, but which seems, in realizing itself, to alter itself or perfect itself according to circumstances. So that, relative to certain qualities, this is an extraordinary appearing variation in the succession of these individuals, and at the same time a constancy which appears wonderful in the entire species. The first animal, the first horse, for example, has been the external model and the interieur mold on which all horses which have been born, all those which now exist, and all those which will be born have been formed.
'Le Cheval', Histoire Naturelle, Générale et Particulière, Avec la Description du Cabinet du Roi (1753), Vol. 4, 215-6. Trans. Phillip R. Sloan.
There is no area in our minds reserved for superstition, such as the Greeks had in their mythology; and superstition, under cover of an abstract vocabulary, has revenged itself by invading the entire realm of thought. Our science is like a store filled with the most subtle intellectual devices for solving the most complex problems, and yet we are almost incapable of applying the elementary principles of rational thought. In every sphere, we seem to have lost the very elements of intelligence: the ideas of limit, measure, degree, proportion, relation, comparison, contingency, interdependence, interrelation of means and ends. To keep to the social level, our political universe is peopled exclusively by myths and monsters; all it contains is absolutes and abstract entities. This is illustrated by all the words of our political and social vocabulary: nation, security, capitalism, communism, fascism, order, authority, property, democracy. We never use them in phrases such as: There is democracy to the extent that… or: There is capitalism in so far as… The use of expressions like “to the extent that” is beyond our intellectual capacity. Each of these words seems to represent for us an absolute reality, unaffected by conditions, or an absolute objective, independent of methods of action, or an absolute evil; and at the same time we make all these words mean, successively or simultaneously, anything whatsoever. Our lives are lived, in actual fact, among changing, varying realities, subject to the casual play of external necessities, and modifying themselves according to specific conditions within specific limits; and yet we act and strive and sacrifice ourselves and others by reference to fixed and isolated abstractions which cannot possibly be related either to one another or to any concrete facts. In this so-called age of technicians, the only battles we know how to fight are battles against windmills.
From 'The Power of Words', collected in Siân Miles (ed.), Simone Weil: An Anthology (2000), 222-223.
There is nothing which Nature so clearly reveals, and upon which science so strongly insists, as the universal reign of law, absolute, universal, invariable law... Not one jot or tittle of the laws of Nature are unfulfilled. I do not believe it is possible to state this fact too strongly... Everything happens according to law, and, since law is the expression of Divine will, everything happens according to Divine will, i.e. is in some sense ordained, decreed.
Lecture 18, 'Predestination and Free-Will', Religion and Science: A Series of Sunday Lectures (1874), 278.
Therefore, these [geotectonic] models cannot be expected to assume that the deeper parts of the earth’s crust were put together and built in a simpler way. The myth about the increasing simplicity with depth results from a general pre-scientific trend according to which the unknown or little known has to be considered simpler than the known. Many examples of this myth occur in the history of geology as, for instance, the development of views on the nature of the seafloor from the past to the present.
In 'Stockwerktektonik und Madelle van Esteinsdifferentiation', in Geotektonisches Symposium zu Ehren von Hans Stille, als Festschrift zur Vollendung seines 80, Lebensjahres (1956), 17, trans. Albert V. and Marguerite Carozzi.
Though much new light is shed by ... studies in radioactivity, the nucleus of the atom, with its hoard of energy, thus continues to present us with a fascinating mystery. ... Our assault on atoms has broken down the outer fortifications. We feel that we know the fundamental rules according to which the outer part of the atom is built. The appearance and properties of the electron atmosphere are rather familiar. Yet that inner citadel, the atomic nucleus, remains unconquered, and we have reason to believe that within this citadel is secreted a great treasure. Its capture may form the main objective of the physicists’ next great drive.
'Assault on Atoms' (Read 23 Apr 1931 at Symposium—The Changing World) Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society (1931), 70, No. 3, 229.
Thus it might be said, that the vegetable is only the sketch, nor rather the ground-work of the animal; that for the formation of the latter, it has only been requisite to clothe the former with an apparatus of external organs, by which it might be connected with external objects.
From hence it follows, that the functions of the animal are of two very different classes. By the one (which is composed of an habitual succession of assimilation and excretion) it lives within itself, transforms into its proper substance the particles of other bodies, and afterwards rejects them when they are become heterogeneous to its nature. By the other, it lives externally, is the inhabitant of the world, and not as the vegetable of a spot only; it feels, it perceives, it reflects on its sensations, it moves according to their influence, and frequently is enabled to communicate by its voice its desires, and its fears, its pleasures, and its pains.
The aggregate of the functions of the first order, I shall name the organic life, because all organized beings, whether animal or vegetable, enjoy it more or less, because organic texture is the sole condition necessary to its existence. The sum of the functions of the second class, because it is exclusively the property of the animal, I shall denominate the animal life.
From hence it follows, that the functions of the animal are of two very different classes. By the one (which is composed of an habitual succession of assimilation and excretion) it lives within itself, transforms into its proper substance the particles of other bodies, and afterwards rejects them when they are become heterogeneous to its nature. By the other, it lives externally, is the inhabitant of the world, and not as the vegetable of a spot only; it feels, it perceives, it reflects on its sensations, it moves according to their influence, and frequently is enabled to communicate by its voice its desires, and its fears, its pleasures, and its pains.
The aggregate of the functions of the first order, I shall name the organic life, because all organized beings, whether animal or vegetable, enjoy it more or less, because organic texture is the sole condition necessary to its existence. The sum of the functions of the second class, because it is exclusively the property of the animal, I shall denominate the animal life.
Physiological Researches on Life and Death (1815), trans. P. Gold, 22-3.
Thus ordered thinking arises out of the ordered course of nature in which man finds himself, and this thinking is from the beginning nothing more than the subjective reproduction of the regularity according to the law of natural phenomena. On the other hand, this reproduction is only possible by means of the will that controls the concatenation of ideas.
An Introduction to Psychology (1912)
To act with common sense according to the moment, is the best wisdom I know; and the best philosophy, to do one’s duties, take the world as it comes, submit respectfully to one’s lot, bless the Goodness that has given so much happiness with it, whatever it is, and despise affectation.
From Letter (27 May 1776) to Horace Mann, collected in Letters of Horace Walpole, Earl of Orford, to Sir Horace Mann (1843), Vol. 2, 378.
To consider the matter aright, reason is nothing but a wonderful and unintelligible instinct in our souls, which carries us along a certain train of ideas, and endows them with particular qualities, according to their particular situations and relations. This instinct, 'tis true, arises from past observation and experience; but can anyone give the ultimate reason, why past experience and observation produces such an effect, any more than why nature alone should produce it?
A Treatise on Human Nature (1739-40), ed. L. A. Selby-Bigge (1888), book 1, part 3, section 16, 179.
To find fault with our ancestors for not having annual parliaments, universal suffrage, and vote by ballot, would be like quarrelling with the Greeks and Romans for not using steam navigation, when we know it is so safe and expeditious; which would be, in short, simply finding fault with the third century before Christ for not being the eighteenth century after. It was necessary that many other things should be thought and done, before, according to the laws of human affairs, it was possible that steam navigation should be thought of. Human nature must proceed step by step, in politics as well as in physics.
The Spirit of the Age (1831). Ed. Frederick A. von Hayek (1942), 48.
To take one of the simplest cases of the dissipation of energy, the conduction of heat through a solid—consider a bar of metal warmer at one end than the other and left to itself. To avoid all needless complication, of taking loss or gain of heat into account, imagine the bar to be varnished with a substance impermeable to heat. For the sake of definiteness, imagine the bar to be first given with one half of it at one uniform temperature, and the other half of it at another uniform temperature. Instantly a diffusing of heat commences, and the distribution of temperature becomes continuously less and less unequal, tending to perfect uniformity, but never in any finite time attaining perfectly to this ultimate condition. This process of diffusion could be perfectly prevented by an army of Maxwell’s ‘intelligent demons’* stationed at the surface, or interface as we may call it with Prof. James Thomson, separating the hot from the cold part of the bar.
* The definition of a ‘demon’, according to the use of this word by Maxwell, is an intelligent being endowed with free will, and fine enough tactile and perceptive organisation to give him the faculty of observing and influencing individual molecules of matter.
* The definition of a ‘demon’, according to the use of this word by Maxwell, is an intelligent being endowed with free will, and fine enough tactile and perceptive organisation to give him the faculty of observing and influencing individual molecules of matter.
In 'The Kinetic Theory of the Dissipation of Energy', Nature (1874), 9, 442.
Truth can only be found by the human intellect, exercised in perfect freedom, and trained to submit itself to the facts of nature. This is the essence of the Scientific Method, which is the exact opposite of the Theological Method. Science teaches men to think with absolute independence of all arbitrary authority, but to submit all their thoughts to the test of actual experiences of Nature. Christianity teaches them to think only according to its own foregone dogmatic conclusions, and to stick to these dogmatic conclusion in defiance of all possible experience.
Leading article in Francis Ellingwood Abbot (ed.), The Index (1 Jan 1880), Volume 11, No. 523, 1.
We have seen that the cytoplasm of nerve has a fluid consistency. Hence its molecules are free to move. According to the thermodynamic principle known as the Gibbs-Thompson rule, any substance in the interior of a liquid which will reduce the free energy of the surface of the liquid, will be concentrated in the surface. The composition of the surface is, therefore, determined by the composition of the fluid from which it is formed; and as the rule is one having universal application, it must hold also for the cytoplasm of nerve. We must think of the surface membrane, then, as a structure which is in equilibrium with the interior of the axon, or at least as one which deviates from equilibrium only because, for dynamic reasons, equilibrium cannot be attained.
With Joseph Erlanger (1874-1965), American physiologist.
With Joseph Erlanger (1874-1965), American physiologist.
Joseph Erlanger and Herbert S. Gasser (eds.), Electrical Signs of Nervous Activity (1937), 136.
We have the opportunity of observing her [Nature] through these delicate and pellucid teguments of the bodies of Insects acting according to her usual course and way, undisturbed, whereas when we endeavour to pry into her secrets by breaking open the doors upon her, and dissecting and mangling creatures whil'st there is life yet within them, we find her indeed at work, but put into such disorder by the violence offer'd, as it may easily be imagin'd how differing a thing we should find, if we could, as we can with a Microscope, in these smaller creatures, quietly peep in at the windows, without frighting her out of her usual byas.
Micrographia, or some Physiological Descriptions of Minute Bodies made by Magnifying Glasses with Observations and Inquiries thereupon (1665), 186.
We may lay it down that a happy person never phantasises, only an unsatisfied one... The motive forces of phantasies are unsatisfied wishes, and every single phantasy is the fulfilment of a wish, a correction of unsatisfying reality. These motivating wishes vary according to the sex, character and circumstances of the person who is having the phantasy; but they fall naturally into two main groups. They are either ambitious wishes, which serve to elevate the subject's personality; or they are erotic ones. It was shocking when Nietzsche said this, but today it is commonplace; our historical position—and no end to it is in sight—is that of having to philosophise without 'foundations'.
Creative Writers and Day-Dreaming (1906), In James Strachey (ed.), The Standard Edition of the Complete Psychcological Works of Sigmund Freud (1959), Vol 9, 146-7.
We may see how unexpectedly recondite parts of pure mathematics may bear upon physical science, by calling to mind the circumstance that Fresnel obtained one of the most curious confirmations of the theory (the laws of Circular Polarization by reflection) through an interpretation of an algebraical expression, which, according to the original conventional meaning of the symbols, involved an impossible quantity.
In History of Scientific Ideas, Bk. 2, chap. 14, sect. 8.
We must examine the moral alchemy through which the in-group readily transmutes virtue into vice and vice into virtue, as the occasion may demand. … We begin with the engagingly simple formula of moral alchemy: the same behavior must be differently evaluated according to the person who exhibits it. For example, the proficient alchemist will at once know that the word “firm” is properly declined as follows:
I am firm,
Thou art obstinate,
He is pig-headed.
There are some, unversed in the skills of this science, who will tell you that one and the same term should be applied to all three instances of identical behavior.
I am firm,
Thou art obstinate,
He is pig-headed.
There are some, unversed in the skills of this science, who will tell you that one and the same term should be applied to all three instances of identical behavior.
In article, 'The Self-Fulfilling Prophecy', The Antioch Review (Summer 1948), 8, No. 2, 195-196. Included as Chap. 7 of Social Theory and Social Structure (1949), 201.
We must keep our freedom of mind, … and must believe that in nature what is absurd, according to our theories, is not always impossible.
In An Introduction to the Study of Experimental Medicine (1927, 1957), 38, as translated by Henry Copley Greene. From the original French by Claude Bernard: “Il faut garder sa liberté d'esprit, et croire que dans la nature l'absurde suivant nos théories n'est pas toujours impossible.” (1865), 67. A Google translation gives: “You have to keep your freedom of mind, … and believe that in nature the absurd according to our theories is not always impossible.”
We must make the following remark: a proof, that after a certain time t1, the spheres must necessarily be mixed uniformly, whatever may be the initial distribution of states, cannot be given. This is in fact a consequence of probability theory, for any non-uniform distribution of states, no matter how improbable it may be, is still not absolutely impossible. Indeed it is clear that any individual uniform distribution, which might arise after a certain time from some particular initial state, is just as improbable as an individual non-uniform distribution; just as in the game of Lotto, any individual set of five numbers is as improbable as the set 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. It is only because there are many more uniform distributions than non-uniform ones that the distribution of states will become uniform in the course of time. One therefore cannot prove that, whatever may be the positions and velocities of the spheres at the beginning, the distributions must become uniform after a long time; rather one can only prove that infinitely many more initial states will lead to a uniform one after a definite length of time than to a non-uniform one. Loschmidt's theorem tells us only about initial states which actually lead to a very non-uniform distribution of states after a certain time t1; but it does not prove that there are not infinitely many more initial conditions that will lead to a uniform distribution after the same time. On the contrary, it follows from the theorem itself that, since there are infinitely many more uniform distributions, the number of states which lead to uniform distributions after a certain time t1, is much greater than the number that leads to non-uniform ones, and the latter are the ones that must be chosen, according to Loschmidt, in order to obtain a non-uniform distribution at t1.
From 'On the Relation of a General Mechanical Theorem to the Second Law of Thermodynamics' (1877), in Stephen G. Brush (ed.), Selected Readings in Physics (1966), Vol. 2, Irreversible Processes, 191-2.
We say that, in very truth the productive cause is a mineralizing power which is active in forming stones… . This power, existing in the particular material of stones, has two instruments according to different natural conditions.
One of these is heat, which is active in drawing out moisture and digesting the material and bringing about its solidification into the form of stone, in Earth that has been acted upon by unctuous moisture… .
The other instrument is in watery moist material that has been acted upon by earthy dryness; and this [instrument] is cold, which … is active in expelling moisture.
One of these is heat, which is active in drawing out moisture and digesting the material and bringing about its solidification into the form of stone, in Earth that has been acted upon by unctuous moisture… .
The other instrument is in watery moist material that has been acted upon by earthy dryness; and this [instrument] is cold, which … is active in expelling moisture.
From De Mineralibus (c.1261-1263), as translated by Dorothy Wyckoff, Book of Minerals (1967), 22.
We set out, therefore, with the supposition that an organised body is not produced by a fundamental power which is guided in its operation by a definite idea, but is developed, according to blind laws of necessity, by powers which, like those of inorganic nature, are established by the very existence of matter. As the elementary materials of organic nature are not different from those of the inorganic kingdom, the source of the organic phenomena can only reside in another combination of these materials, whether it be in a peculiar mode of union of the elementary atoms to form atoms of the second order, or in the arrangement of these conglomerate molecules when forming either the separate morphological elementary parts of organisms, or an entire organism.
Mikroskopische Untersuchungen über die Uebereinstimmung in der Struktur und dem Wachsthum der Thiere und Pflanzen (1839). Microscopic Researches into the Accordance in the Structure and Growth of Animals and Plants, trans. Henry Smith (1847), 190-1.
What really matters for me is … the more active role of the observer in quantum physics … According to quantum physics the observer has indeed a new relation to the physical events around him in comparison with the classical observer, who is merely a spectator.
Letter to Niels Bohr (1955). Quoted in Robert J. Scully, The Demon and the Quantum (2007), 22.
What these two sciences of recognition, evolution and immunology, have in common is not found in nonbiological systems such as 'evolving' stars. Such physical systems can be explained in terms of energy transfer, dynamics, causes, and even 'information transfer'. But they do not exhibit repertoires of variants ready for interaction by selection to give a population response according to a hereditary principle. The application of a selective principle in a recognition system, by the way, does not necessarily mean that genes must be involved—it simply means that any state resulting after selection is highly correlated in structure with the one that gave rise to it and that the correlation continues to be propagated. Nor is it the case that selection cannot itself introduce variation. But a constancy or 'memory' of selected events is necessary. If changes occurred so fast that what was selected could not emerge in the population or was destroyed, a recognition system would not survive. Physics proper does not deal with recognition systems, which are by their nature biological and historical systems. But all the laws of physics nevertheless apply to recognition systems.
Bright and Brilliant Fire, On the Matters of the Mind (1992), 79.
What, then, is light according to the electromagnetic theory? It consists of alternate and opposite rapidly recurring transverse magnetic disturbances, accompanied with electric displacements, the direction of the electric displacement being at the right angles to the magnetic disturbance, and both at right angles to the direction of the ray.
'A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field' (1864). In W. D. Niven (ed.), The Scientific Letters and Papers of James Clerk Maxwell(1890), Vol. 2, 1862-1973, 195.
Whatever opinions we may adopt as to the physical constitution of comets, we must admit that they serve some grand and important purpose in the economy of the universe; for we cannot suppose that the Almighty has created such an immense number of bodies, and set them in rapid motion according to established laws, without an end worthy of his perfections, and, on the whole, beneficial to the inhabitants of the system through which they move.
In The Sidereal Heavens and Other Subjects Connected with Astronomy: As Illustrative of the Character of the Deity, and of an Infinity of Worlds (1871), 353.
When I read an Italian letter [Saggio by Voltaire] on changes which had occurred on the surface of the earth, published in Paris this year (1746), I believed that these facts were reported by La Loubère. Indeed, they correspond perfectly with the author’s ideas. Petrified fish are according to him merely rare fish thrown away by Roman cooks because they were spoiled; and with respect to shells, he said that they were from the sea of the Levant and brought back by pilgrims from Syria at the time of the crusades. These shells are found today petrified in France, in Italy and in other Christian states. Why did he not add that monkeys transported shells on top of high mountains and to every place where humans cannot live? It would not have harmed his story but made his explanation even more plausible.
In 'Preuves de la Théorie de la Terre', Histoire Naturelle, Générale et Particuliere, Avec la Description du Cabinet du Roi (1749), Vol. I, 281. Trans. Albert V. and Marguerite Carozzi.
When I undertake the dissection of a human cadaver I pass a stout rope tied like a noose beneath the lower jaw and through the two zygomas up to the top of the head, either more toward the forehead or more toward the occiput according as I want the cadaver to hang with its head up or down. The longer end of the noose I run through a pulley fixed to a beam in the room so that I may raise or lower the cadaver as it hangs there or may turn it round in any direction to suit my purpose; and should I so wish I can allow it to recline at an angle upon a table, since a table can easily be placed underneath the pulley. This is how the cadaver was suspended for drawing all the muscle tables... though while that one was being drawn the rope was passed around the occiput so as to show the muscles in the neck. If the lower jaw has been removed in the course of dissection, or the zygomas have been broken, the hollows for the temporal muscles will nonetheless hold the noose sufficiently firmly. You must take care not to put the noose around the neck, unless some of the muscles connected to the occipital bone have already been cut away. It is best to suspend the cadaver like this because a human body lying on a table is very difficult to turn over on to its chest or its back.
From De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem (1543), Book II, 268, as translated by William Frank Richardson and John Burd Carman, in 'How the Cadaver Can Be Held Erect While These Muscles are Dissected', On The Fabric of the Human Body: Book II: The Ligaments and Muscles (1998), 234.
When it is not in our power to determine what is true, we ought to act according to what is most probable.
In Discours de la Méthode: Troisième partie, collected in Oeuvres Philosophiques de Descartes (1835), 23. As quoted and translated in Joseph William Mellor, Higher Mathematics for Students of Chemistry and Physics (1901), 416. From the original French, “Lorsqu’il n’est pas eu notre pouvoir de discerner les plus vraies opinions, nous devons suivre les plus probables.”
When the elements are arranged in vertical columns according to increasing atomic weight, so that the horizontal lines contain analogous elements again according to increasing atomic weight, an arrangement results from which several general conclusions may be drawn.
'The Relations of the Properties to the Atomic Weights of the Elements', Zeitschrift fur Chemie, 1869.
When... the biologist is confronted with the fact that in the organism the parts are so adapted to each other as to give rise to a harmonious whole; and that the organisms are endowed with structures and instincts calculated to prolong their life and perpetuate their race, doubts as to the adequacy of a purely physiochemical viewpoint in biology may arise. The difficulties besetting the biologist in this problem have been rather increased than diminished by the discovery of Mendelian heredity, according to which each character is transmitted independently of any other character. Since the number of Mendelian characters in each organism is large, the possibility must be faced that the organism is merely a mosaic of independent hereditary characters. If this be the case the question arises: What moulds these independent characters into a harmonious whole? The vitalist settles this question by assuming the existence of a pre-established design for each organism and of a guiding 'force' or 'principle' which directs the working out of this design. Such assumptions remove the problem of accounting for the harmonious character of the organism from the field of physics or chemistry. The theory of natural selection invokes neither design nor purpose, but it is incomplete since it disregards the physiochemical constitution of living matter about which little was known until recently.
The Organism as a Whole: From a Physiochemical Viewpoint (1916), v-vi.
Where the untrained eye will see nothing but mire and dirt, Science will often reveal exquisite possibilities. The mud we tread under our feet in the street is a grimy mixture of clay and sand, soot and water. Separate the sand, however, as Ruskinn observes—let the atoms arrange themselves in peace according to their nature—and you have the opal. Separate the clay, and it becomes a white earth, fit for the finest porcelain; or if it still further purifies itself, you have a sapphire. Take the soot, and it properly treated it will give you a diamond. While lastly, the water, purified and distilled, will become a dew-drop, or crystallize into a lovely star. Or, again, you may see as you will in any shallow pool either the mud lying at the bottom, or the image of the heavens above.
The Pleasures of Life (1887, 2007), 63.
While all bodies are composed of the four elements, that is, of heat, moisture, the earthy, and air, yet there are mixtures according to natural temperament which make up the natures of all the different animals of the world, each after its kind.
In De Architectura, Book 1, Chap 4, Sec. 5. As translated in Morris Hicky Morgan (trans.), Vitruvius: The Ten Books on Architecture (1914), 16.
While we keep an open mind on this question of vitalism, or while we lean, as so many of us now do, or even cling with a great yearning, to the belief that something other than the physical forces animates the dust of which we are made, it is rather the business of the philosopher than of the biologist, or of the biologist only when he has served his humble and severe apprenticeship to philosophy, to deal with the ultimate problem. It is the plain bounden duty of the biologist to pursue his course unprejudiced by vitalistic hypotheses, along the road of observation and experiment, according to the accepted discipline of the natural and physical sciences. … It is an elementary scientific duty, it is a rule that Kant himself laid down, that we should explain, just as far as we possibly can, all that is capable of such explanation, in the light of the properties of matter and of the forms of energy with which we are already acquainted.
From Presidential Address to Zoological Section of the British Association for the Advancement of Science. As quoted in H.V. Neal, 'The Basis of Individuality in Organisms: A Defense of Vitalism', Science (21 Jul 1916), 44 N.S., No. 1125, 82.
With whom [do] the adherents of historicism actually empathize[?] The answer is inevitable: with the victor. And all rulers are the heirs of those who conquered before them. Hence, empathy with the victor invariably benefits the rulers. Historical materialists know what that means. Whoever has emerged victorious participates to this day in the triumphal procession in which the present rulers step over those who are lying prostrate. According to traditional practice, the spoils are carried along in the procession. They are called cultural treasures, and a historical materialist views them with cautious detachment. For without exception the cultural treasures he surveys have an origin which he cannot contemplate without horror. They owe their existence not only to the efforts of the great minds and talents who have created them, but also to the anonymous toil of their contemporaries. There is no document of civilization which is not at the same time a document of barbarism.
'Theses on the Philosophy of History' (completed 1940, first published 1950). In Illuminations, ed. Hannah Arendt and trans. Harry Zohn (1970), 258.
Yet man does recognise himself [as an animal]. But I ask you and the whole world for a generic differentia between man and ape which conforms to the principles of natural history, I certainly know of none... If I were to call man ape or vice versa, I should bring down all the theologians on my head. But perhaps I should still do it according to the rules of science.
Letter to Johann Gmelon (14 Jan 1747), quoted in Mary Gribbin, Flower Hunters (2008), 56.
You say Beasts are Machines like Watches? But put the Machine called a Dog, and the Machine called a Bitch to one another for some time, and there may result another little Machine; whereas two Watches might be together all their Life-time, without ever producing a third Watch. Now Madam de B— and I think, according to our Philosophy, that all things which being but two, are endued with the Virtue of making themselves three, are of a much higher Nature than a Machine.
'Letter XI to Mr. C: Upon his studying the Philosophy of Descartes', Letters of Gallantry (1685), trans. Mr Ozell (1715), 25.








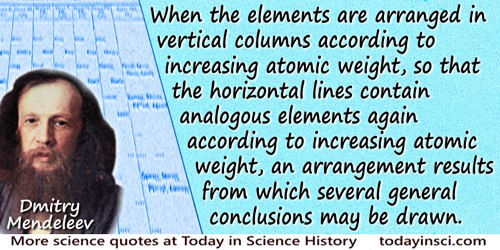
 In science it often happens that scientists say, 'You know that's a really good argument; my position is mistaken,' and then they would actually change their minds and you never hear that old view from them again. They really do it. It doesn't happen as often as it should, because scientists are human and change is sometimes painful. But it happens every day. I cannot recall the last time something like that happened in politics or religion.
(1987) --
In science it often happens that scientists say, 'You know that's a really good argument; my position is mistaken,' and then they would actually change their minds and you never hear that old view from them again. They really do it. It doesn't happen as often as it should, because scientists are human and change is sometimes painful. But it happens every day. I cannot recall the last time something like that happened in politics or religion.
(1987) -- 


